Table of Contents
Updated on February 17, 2026 with new data.
A modern go-to-market (GTM) strategy relies on more than just talent and timing—it hinges on the technology stack that supports it. With the surge in SaaS tools and AI-powered platforms, businesses are reevaluating how they structure and integrate their go-to-market (GTM) technology stacks. The right stack not only powers sales and marketing activities but also enables cross-functional alignment, data-driven decisions, and faster execution across the entire revenue team.
The number of software solutions continues to grow, reaching over 15,000 tools by 2025 alone. The pressure to build and manage a focused, effective GTM tech stack is higher than ever. Understanding what this stack includes, why it matters, and how to optimize it is essential for any company looking to compete in today’s crowded markets.
What Is a GTM Tech Stack?
A GTM tech stack is the collection of tools and platforms a business uses to support its go-to-market strategy. It includes software that enables marketing, sales, customer success, and operations teams to engage prospects, convert leads, and drive revenue. This stack typically spans CRM systems, marketing automation platforms, sales engagement tools, customer data platforms, and analytics software.
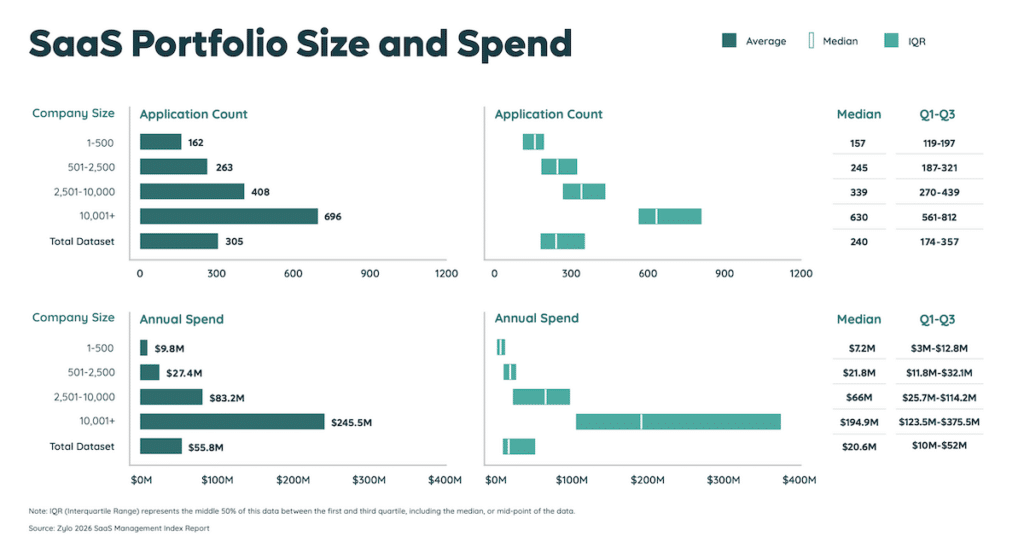
While every company’s stack varies based on size, industry, and sales model, the goal is the same: to create a connected ecosystem that empowers teams to reach buyers more effectively. As AI capabilities grow and SaaS portfolios expand, averaging 305 apps per organization in 2024, building a lean, aligned stack has become both a challenge and a competitive advantage.
Why a Go-to-Market Tech Stack Is Important
Your go-to-market tech stack influences everything from pipeline velocity to customer retention. When it’s built strategically, it helps teams deliver consistent, personalized experiences across the buyer journey. It also gives leadership visibility into what’s working and where deals are stalling, enabling better resource allocation and smarter growth decisions.
A fragmented stack, by contrast, creates silos and inefficiencies. Tools that don’t integrate or overlap in functionality increase spend while reducing impact. In a market with over 15,000 martech solutions and climbing, according to Chief Martec’s 2025 report, organizations that invest in centralized stack management gain a measurable edge in agility and performance.

How a GTM Tech Stack Improves Sales and Marketing Alignment
One of the most significant benefits of a robust GTM stack is the tighter alignment between sales and marketing. Shared platforms like CRMs and MAPs ensure both teams operate from a single source of truth. Automation tools streamline lead handoff, while shared reporting creates accountability around performance.
When marketing can see which content drives conversions and sales can track engagement in real time, both teams are more informed and effective. Go-to-market stacks that integrate usage and spend data help revenue teams prioritize high-value tools and eliminate friction across the sales funnel.
GTM Tech Stack Components And Tools
Building a modern go-to-market tech stack involves selecting the right mix of tools to support each stage of the customer journey. From first-touch engagement to closed and beyond, every team in the revenue engine needs visibility, automation, and actionable insights. The best stacks are integrated, flexible, and purpose-built for collaboration.
Marketing Automation Tools
Marketing automation platforms (MAPs) serve as the backbone of outbound engagement. These tools manage email campaigns, lead scoring, audience segmentation, and other key functions. When used effectively, MAPs enable consistent messaging at scale while tracking performance in real-time. Popular platforms like HubSpot and Marketo help teams move faster while integrating seamlessly with sales tools and CRMs.
MAPs also play a growing role in personalization. With AI-enhanced content generation and dynamic audience targeting becoming the norm, marketing automation is no longer just about efficiency—it’s about creating more relevant buyer experiences.
Sales Enablement Tools
Sales enablement software equips representatives with the content, context, and automation they need to close deals more efficiently. These tools often include conversation intelligence, guided selling workflows, and engagement tracking. When tightly integrated with marketing and CRM platforms, sales enablement solutions keep teams aligned and ensure content is used at the right time in the buyer journey.
In high-performing GTM stacks, enablement tools help bridge the gap between strategy and execution. Reps don’t waste time searching for materials, and marketers gain visibility into which assets are driving revenue.
CRM
The customer relationship management platform (CRM) is often considered the center of the GTM tech stack, especially for B2B companies. It provides a centralized system for tracking contacts, accounts, opportunities, and pipeline progress. CRMs like Salesforce or HubSpot offer integrations with sales, marketing, and customer success tools, enabling a unified view of customer data.
Data shows that CRMs are still the dominant core for GTM stacks among B2B organizations, with 42% citing them as their central platform. Centralization is essential for data integrity, forecasting, and alignment across revenue teams.
Data Intelligence
Data intelligence platforms turn GTM data into actionable insights. They aggregate usage data, account activity, and engagement signals to help teams prioritize high-intent buyers and optimize outreach strategies.
Tools like 6Sense and ZoomInfo support this by offering advanced lead scoring, buyer intent signals, and pipeline analytics that help revenue teams engage the right accounts at the right time..
Integrated intelligence also enhances personalization and timing—two key factors in achieving success with your go-to-market stack. With the rise of AI, expect data intelligence to play an even larger role in identifying patterns and surfacing next-best actions across the funnel.
Customer Success Tools
Customer success platforms are an increasingly important part of the GTM stack, especially in subscription-based models. These tools track health scores, manage renewals, and trigger outreach when accounts show signs of churn risk or expansion opportunity. Aligning post-sale activities with marketing and sales data helps close the loop and improve customer lifetime value.
Platforms like Gainsight and Totango provide visibility into account behavior and outcomes, enabling more proactive engagement. When customer success is integrated into your go-to-market stack, feedback flows back to product and marketing in real-time.
AI and Automation Layers
AI is more than something that’s nice-to-have. As AI capabilities advance, it’s becoming a foundational element of many go-to-market tech stacks. From generative content to automated lead routing and predictive scoring, AI is reshaping how GTM teams work. Tools like Gong, Clari, and Drift are embedding AI into sales and marketing workflows, helping teams do more with less.
AI-powered solutions are largely responsible for the recent expansion of the stack. With 78% of marketers now using AI for content production and over 40% for audience targeting, these capabilities are becoming core components, not bolt-ons.
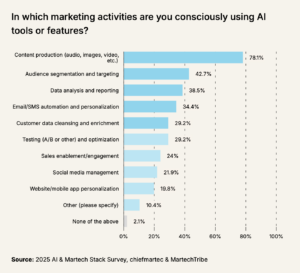
Integration and Management Tools
No stack functions well without strong integration and governance. Tools that manage app visibility, usage, and cost play a vital role in keeping the GTM ecosystem efficient. Without them, teams risk developing shadow IT, incurring budget waste, and creating data silos.
Centralized management helps ensure that each tool delivers a satisfactory return on investment (ROI) and that the stack evolves in line with the organization’s needs. As stacks grow past 275 apps, oversight becomes non-negotiable.
How to Optimize Your Go-to-Market Tech Stack
As GTM strategies evolve, so must the technology that powers them. An optimized GTM tech stack is about much more than just having the latest tools. It ensures each tool drives impact, integrates smoothly, and supports core business goals. Optimization is an ongoing process that requires strategic evaluation and cross-functional input.
Define Goals and Objectives
Before making changes, clarify what success looks like for your GTM stack. Are you aiming to shorten the sales cycle, improve pipeline accuracy, reduce customer acquisition cost, or increase retention?
Specific goals will determine which tools stay, which ones go, and which ones need to be added. Without a clear target, even the most advanced tech won’t deliver meaningful results.
Goals should be shared across sales, marketing, customer success, and operations to ensure the entire stack supports unified outcomes, and not just departmental KPIs.
Assess the Current Tech Stack
Begin by documenting all the tools currently in use. This includes software licensed by IT, apps brought in by individual teams, and even free tools adopted without oversight.
This is important, because many companies underestimate the number of SaaS tools they’re actually using by nearly 2X. Today, companies have 275 apps on average, with shadow IT often accounting for a significant share.
By building a comprehensive inventory, you gain the visibility necessary to assess spending, usage, and integration gaps.
Analyze Tool Effectiveness
Once your stack is mapped, evaluate how well each tool is performing. Are platforms actively used by the intended teams? Are they delivering measurable ROI? Are critical features underutilized?
Usage data—such as what Zylo provides through Application Usage Insights—can uncover which tools drive business outcomes and which may be draining resources. These insights are essential for rationalizing the stack and uncovering hidden inefficiencies.
Eliminate Redundant Tools
Redundancy is one of the most common causes of bloat in a GTM stack. Multiple tools often serve the same function across departments without offering differentiated value. Not only does this waste budget, but it also fragments data and creates inconsistent processes.
Look for overlap in categories like CRM, sales engagement, or marketing automation. Consolidating around a single platform can improve efficiency and data hygiene.
The “godfather of the martech landscape” Scott Brinker talks about app consolidation as a double-edged sword. On one hand, your GTM tech stack is tighter with less waste. On the other hand, it’s easy to become deeply embedded in a specific vendor, which makes it harder to switch when you need to. Watch the clip below to hear more.
Use Automation
Automation helps scale GTM efforts without adding headcount. From lead scoring and email sequences to renewal reminders and contract workflows, automated processes save time and reduce manual errors. Modern GTM stacks should also use automation for analyses—surfacing trends, anomalies, and optimization opportunities.
AI further enhances automation with predictive insights and personalized experiences, helping teams stay ahead of buyer expectations.
Align Tools and Business Goals
Every tool in your stack should map to a specific business objective. If a platform doesn’t support your GTM goals—whether that’s accelerating deals, improving attribution, or deepening customer insights—it may be time to phase it out.
Alignment also means ensuring tools are used to their full potential. Underutilized platforms often stem from a lack of training or poor integration, rather than a poor product-market fit.
Involve Cross-Functional Stakeholders
Optimization isn’t a solo effort. Involve leaders from marketing, sales, CS, IT, and finance to ensure the stack meets the needs of every function. This prevents siloed decision-making and ensures that each tool contributes to shared success metrics.
Cross-functional input also helps reduce resistance to change and encourages broader adoption when tools are added, removed, or replaced.
Establish a Stack Governance Framework
To keep your GTM stack optimized long term, create clear processes for tool requests, evaluations, renewals, and decommissions. A governance framework reduces the risk of shadow IT and ensures that each tool has an owner responsible for usage, performance, and integration.
It’s possible that your procurement or finance team already has policies in place. Work with them to understand what framework already exists that your GTM team can adopt—instead of starting from scratch.
Zylo’s SaaS Governance and Risk Mitigation solution is one example of how organizations can enforce policies that keep the tech stack lean, compliant, and aligned.
Popular GTM Tech Stack Tools
While no two companies use the exact same stack, certain tools have become foundational in the go-to-market tech ecosystem. These platforms consistently support marketing, sales, and customer success teams in delivering results.
Top GTM stack tools include:
- CRM: Salesforce, HubSpot
- Marketing Automation: Marketo, Pardot, ActiveCampaign
- Sales Enablement: Outreach, Salesloft, Gong
- Customer Success: Gainsight, Totango
- Data and Intelligence: ZoomInfo, 6sense, Clari
- Analytics and Attribution: Tableau, Looker, Bizible
- Collaboration and Ops: Slack, Notion, Asana, Zapier
Many of these tools now include AI features, such as guided selling, generative content, and predictive insights. As Zylo’s SaaS Visibility & Inventory Management data shows, understanding which tools drive value—and eliminating those that don’t—is key to optimizing stack performance.
Future Trends in GTM Tech Stack
As technology evolves, so do the expectations placed on GTM stacks. Several emerging trends are reshaping how companies build and manage their systems.
- AI Integration and Agentic Workflows: AI is moving from isolated use cases to being deeply embedded in martech. The State of Martech 2025 report highlights the rise of AI assistants and agentic flows—automated sequences powered by large language models that act autonomously across systems.
- Composable Architecture: Instead of relying on all-in-one suites, companies are assembling best-of-breed tools connected through APIs and cloud data warehouses. This enables more flexibility and scalability.
- Governance and Spend Optimization: As stacks expand again (averaging 275 apps in 2024), organizations are investing in governance to manage risk, cost, and tool sprawl more proactively.
- Shift Toward Unified Data Layers: The adoption of cloud data warehouses like Snowflake and Databricks continues to grow. These serve as a backbone for integrated insights and AI-driven decision-making across the stack.
“Suite [solutions] really do need to give way to platform ecosystems.”
— Scott Brinker, Editor, Chiefmartec
Challenges of Managing a GTM Tech Stack
One aspect many overlook is the challenges organizations face when maintaining and scaling a GTM stack.
Fragmented data, overlapping functionality, rising costs, and low adoption rates all limit performance. Teams often struggle to answer simple questions like: “Which tools are actually being used?” or “How much are we spending per function?”
These challenges reinforce the need for robust SaaS management, clear stack ownership, and usage analytics—capabilities that tools like Zylo’s SaaS License Management address directly.
FAQ About GTM Tech Stacks
What Is a GTM Tech Stack?
A GTM tech stack is the collection of software tools a company uses to bring products or services to market. It supports every stage of the customer journey—from lead generation to deal close and retention—across marketing, sales, and customer success.
What Does GTM Stand for in Tech?
In tech, GTM stands for “Go-to-Market.” It refers to the strategy and execution plan a company uses to launch and scale its offerings. The GTM tech stack includes the tools used to support and streamline this strategy.
What Are GTM Tools?
GTM tools are software platforms that support go-to-market functions, including campaign execution, lead management, sales engagement, and customer onboarding. These tools help teams coordinate efforts and track results.
Which Tools Are Commonly Included in a GTM Tech Stack?
Most GTM stacks include a CRM, marketing automation software, sales enablement tools, and analytics platforms. Larger organizations may also use customer success platforms, product analytics tools, and spend management solutions to round out their stack.
How Do You Know If Your GTM Stack Is Working?
To evaluate your GTM stack, look at tool usage, adoption rates, ROI metrics, and integration health. If platforms are underused or data is siloed, it may be time to consolidate or replace parts of your stack.
Can a GTM Stack Be Too Large?
Yes. When stacks grow without oversight, teams may face duplicated features, inconsistent data, and rising costs. Zylo’s research shows that stacks have started expanding again, making governance and optimization more important than ever.
Gain Full Control of Your GTM Tech Stack With Zylo
As the GTM landscape grows more complex, so does the challenge of managing the tools behind it. Without visibility, alignment, and governance, even the best-intentioned tech stacks can underperform. Zylo helps you take control, giving your organization the insights it needs to eliminate waste, improve adoption, and scale smarter.
With solutions for SaaS visibility, license management, and spend optimization, Zylo empowers GTM leaders to build leaner, more effective stacks that support real growth.
Whether you’re auditing your existing tools or preparing to scale, Zylo provides the foundation to make confident, data-backed decisions about every app in your portfolio.


 — Scott Brinker, Editor, Chiefmartec
— Scott Brinker, Editor, Chiefmartec