Table of Contents
Managing SaaS agreements effectively is a cornerstone of strong SaaS governance. With the growing reliance on subscription-based tools, businesses must ensure their agreements are clear, comprehensive, and aligned with organizational goals. A well-structured SaaS agreement helps define expectations, minimize risks, and provide the foundation for a successful vendor partnership.
This checklist will guide you through the key elements to evaluate when reviewing or negotiating SaaS agreements—whether standard SaaS agreements or more complex contracts like SELAs. From ensuring transparency in the contract terms to aligning contract details with your broader software strategy, these steps will help you optimize your SaaS investments and reduce potential pitfalls.
What Is a SaaS Agreement?
A SaaS agreement is a contract between a business and a SaaS provider that outlines the terms for accessing and using subscription-based software. Unlike traditional software licenses, SaaS agreements focus on granting access to cloud-based solutions rather than transferring ownership. These agreements are essential for defining how the service will operate, what the provider is responsible for, and the customer’s obligations.
Key components typically include service availability, data privacy, security measures, payment terms, and usage restrictions. With SaaS platforms forming the backbone of modern business operations, having a clear and well-defined agreement ensures both parties are protected while enabling the business to leverage the software effectively.
Why SaaS Agreements Are Essential
SaaS agreements are pivotal in safeguarding the relationship between businesses and software providers. They ensure that expectations around service delivery, uptime, data security, and usage rights are clearly defined, helping to prevent misunderstandings and reduce risks. These agreements also set the foundation for managing compliance with regulations, protecting sensitive data, and outlining dispute resolution procedures.
Given their importance, you need to approach SaaS contracts strategically. Our guide to SaaS contracts provides a deeper dive into key considerations when negotiating and reviewing these contracts. By understanding the nuances, you can ensure your agreements align with organizational goals and provide flexibility for evolving needs.
When You Need a SaaS Agreement
A SaaS agreement is essential whenever your organization adopts a cloud-based software solution. These agreements are the backbone of your relationship with the provider, ensuring clarity around the terms of service, pricing, and responsibilities. Whether integrating a critical tool for your operations or testing a niche application, a well-structured SaaS agreement is necessary to protect your organization’s interests.
Beyond legal protection, SaaS agreements help you establish key operational parameters, such as uptime guarantees, support availability, and data ownership rights. They’re especially important when dealing with sensitive information or services that are integral to your workflow, as they provide a clear framework for accountability and recourse in case of disruptions. By securing a robust agreement, your organization can operate with confidence while maintaining compliance and mitigating risk.
SaaS Agreement Checklist: 23 Things to Review in Every SaaS Contract
This SaaS agreement checklist helps maximize the value of your software subscriptions. Look for these 23 essential details in every agreement to improve your SaaS management:
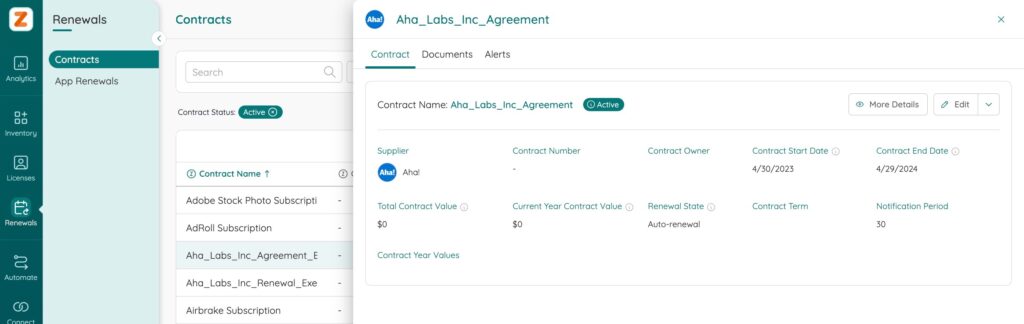
1. Start Date
The agreement start date may also be known as the commencement date or effective date. This is when your software-as-a-service agreement officially activates, and the subscription becomes available to the company or its end-users. Knowing the exact agreement kickoff date is important, because all agreement term durations tie back to this date.
2. End Date
The critical second step of the SaaS agreement checklist is knowing the SaaS agreement end date. This date may also be referred to as the renewal date or termination date.
It’s important to anticipate renewal dates so that application owners or sourcing teams have sufficient lead time to proactively negotiate contract renewal terms and ensure you obtain maximum value from the subscription. Starting renewal or offboarding planning or negotiations ahead of the curve is beneficial in SaaS agreement discussions.
Having trouble locating this information? Look for the termination section in your SaaS agreement.
3. Subscription Renewal and Notification Periods
Notification periods are critical to SaaS agreements, especially when it comes to managing subscription renewals effectively. Most providers require customers to notify them in advance if they do not intend to renew their contract automatically. For example, if a SaaS agreement specifies a 60-day notification period, the customer must communicate their intent not to renew at least 60 days before the contract end date.
According to Zylo data, 30-day notification periods are the most common, followed by 60-day and 90-day periods. Shorter periods, such as 15 days, do appear occasionally, while longer periods of 180 days or more are rare but not unheard of. Organizations without a system to track these requirements often face challenges in meeting notification deadlines, risking unintended renewals or lapses in service.
4. Auto-Renewal Clauses
Many SaaS agreements include auto-renewal clauses that automatically extend the contract unless timely notice is provided. These clauses are intended to ensure uninterrupted service but can lead to unintended renewals if not carefully managed. Reviewing key elements of auto-renewal terms, such as renewal periods, notification deadlines, and any changes to pricing or terms upon renewal, helps maintain control over your SaaS subscriptions.
Using a SaaS system of record like Zylo simplifies renewal management by centralizing agreement terms and providing proactive alerts for both notification and auto-renewal deadlines. This ensures IT leaders and business units stay informed, enabling smarter renewal decisions and reducing the risk of unplanned expenses.
If you can’t find details about notification or auto-renewal clauses, check your contracts’ termination or renewal section. Including this step in your SaaS agreement checklist is vital to maintaining flexibility and control over your subscription portfolio.
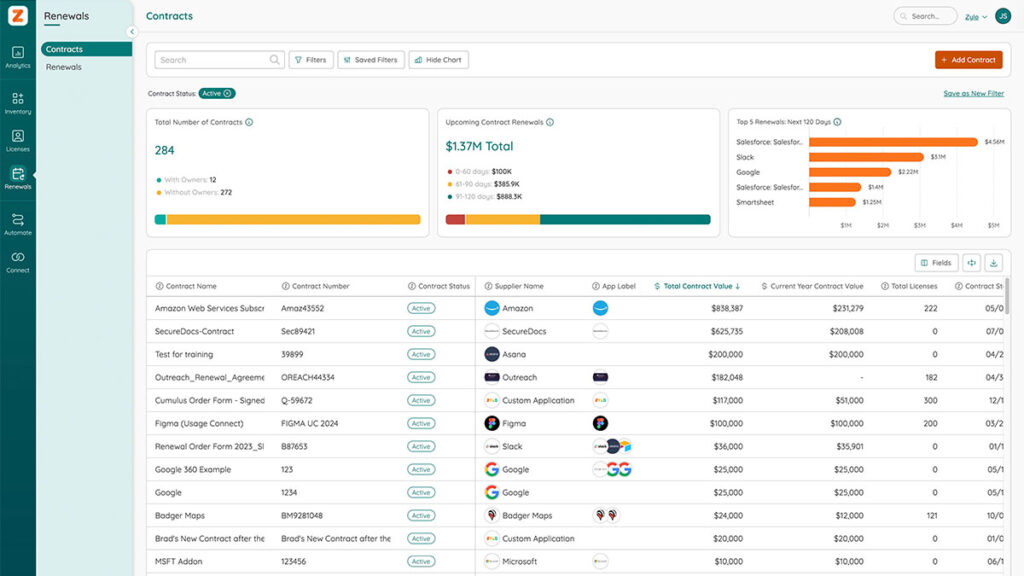
5. Total SaaS Contract Value (TCV)
The total contract value (TCV) represents the combined financial commitments for all SaaS subscriptions across an organization’s business units. Understanding TCV is essential to ensure alignment between agreement terms and actual spending, as gaps between the two can signal inefficiencies or hidden costs.
For instance, if the original contract commits to $10,000 but billing data indicates the organization is spending significantly more, it’s crucial to investigate the discrepancy. Differences between committed and actual spending often highlight upgrades, overages, or cost escalators like additional features or shifts in pricing models. Identifying these factors enables businesses to address unnecessary expenses and take control of their SaaS spend.
Regularly reviewing TCV as part of your SaaS agreement management process ensures your organization optimizes costs and maintains financial transparency across subscriptions.
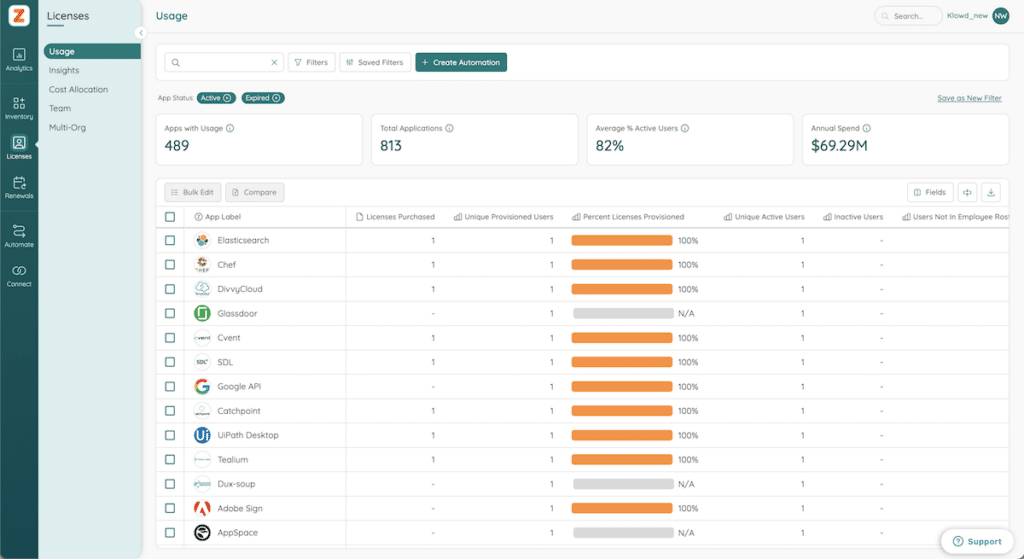
6. Total Quantity and Types of SaaS Licenses
SaaS subscriptions often include a specific number of licenses allocated across an organization. However, unused or mismanaged licenses can lead to unnecessary expenses without proper oversight. For instance, if employees fail to adopt the software fully or licenses remain assigned after personnel changes, your organization risks wasting resources on underutilized subscriptions.
Regularly comparing active user accounts and actual usage data against the number of purchased licenses allows you to pinpoint gaps and uncover opportunities to save costs. Proactive license management ensures efficient use of your SaaS investments and helps optimize spending across business units, preventing losses and maximizing value. Including this step in your SaaS agreement checklist is a straightforward way to enhance your subscription management strategy.
7. Billing Frequency and Payment Terms
Understanding how and when payments are made is essential for managing SaaS subscriptions effectively. These terms outline the timing and structure of payments, helping organizations manage cash flow and assess the return on investment (ROI) of their software solutions.
SaaS agreements typically offer various billing frequency options, such as monthly, semi-annual, annual, multi-year, or single-purchase plans. In addition to frequency, agreements often include critical details like:
- Payment Milestones: Specific points in the subscription cycle when payments are due, such as upfront payment for an annual plan or milestone payments for longer-term agreements.
- Due Dates: The exact date when payments must be received to maintain uninterrupted service.
- Acceptable Payment Methods: The methods the provider supports, such as credit card, bank transfer, or ACH payment. Ensuring compatibility with your organization’s preferred payment systems can prevent delays.
- Late Payment Penalties: Terms outlining any additional charges or service disruptions that may occur if payments are late. Reviewing these clauses helps avoid unforeseen costs.
Including these details in your SaaS agreement checklist ensures you’re well-prepared to meet financial obligations and avoid payment-related issues. This proactive approach supports better financial planning and fosters strong vendor relationships.
8. Consumption Metrics and Billing Units
Tracking consumption metrics and billing units is essential to managing SaaS contracts. These metrics define how usage is measured and priced, offering a clear view of costs tied to application usage. By identifying and monitoring these metrics, organizations can better plan their SaaS budgets, prevent unexpected overages, and ensure their software investments align with actual needs.
What are SaaS consumption metrics? They are units of value tied to pricing, each with a predefined limit or capacity. These metrics are outlined in the SaaS agreement and play a critical role in understanding and managing costs. Examples of common consumption metrics include:
- Total quantity of emails sent through email marketing platforms like Mailchimp, Salesforce Marketing Cloud, or Constant Contact.
- Total envelopes used in contract lifecycle management tools.
- Total storage capacity in cloud storage platforms like Box or Dropbox.
- Total unique projects managed in collaboration tools such as Asana, Trello, or Basecamp.
Including consumption metrics in your SaaS agreement checklist ensures that you can proactively monitor usage, identify inefficiencies, and adjust your strategy as needed. This approach helps contain costs and supports more accurate financial forecasting for organization-wide SaaS management.
9. Data Handling, Privacy, and Security
Managing data effectively in a SaaS agreement goes beyond usage; it requires clear definitions of how data is stored, secured, and transferred. Organizations must ensure that critical data remains accessible and protected, even if the contract ends. A well-structured agreement prevents the risk of feeling locked into a provider out of fear of losing access to essential information.
Data privacy and security measures should be explicitly addressed in the agreement. Vendors should outline their processes for protecting data, such as encryption standards, backup procedures, and access controls. Clarify what happens to your data upon contract termination, including timelines for data handover and deletion to avoid potential breaches or loss. This level of detail ensures transparency and gives your organization greater confidence in its SaaS partnerships.
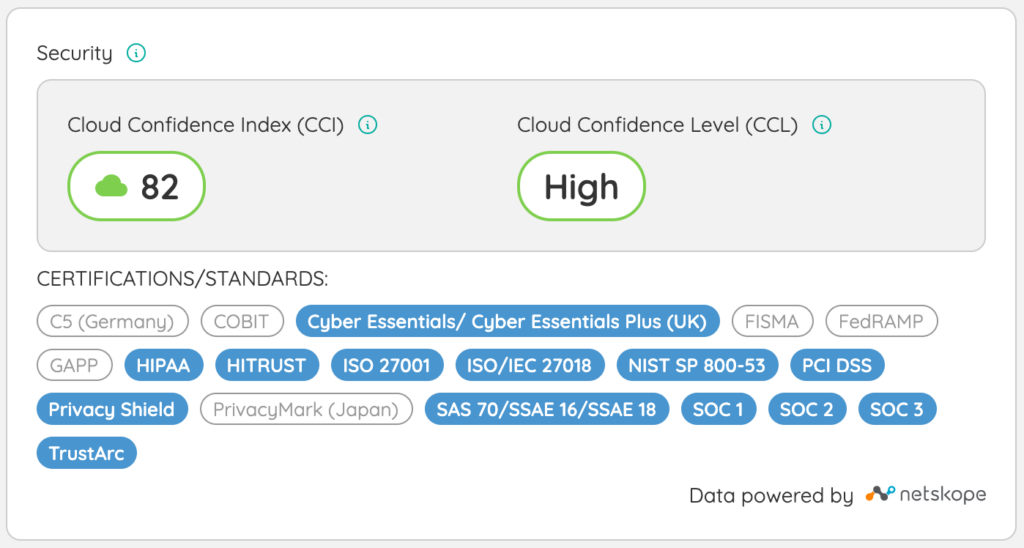
10. Regulatory Compliance
When selecting SaaS vendors subject to data protection regulations like GDPR, SOC II, or CCPA, your organization must confirm that providers meet the required standards and document compliance details in the SaaS agreement. Key elements to review are the vendor’s certification levels, reporting practices, and procedures for addressing non-compliance.
By separating compliance requirements into a clear section of the SaaS agreement, your organization can reduce legal risks and maintain trust in vendor relationships. Using a platform like Zylo helps streamline compliance tracking with customizable fields and centralized agreement management, making it easier to ensure vendors align with your obligations.
11. Line-Item Details
For any SaaS subscription, it’s important to have a clear understanding of consumption metrics and thresholds for usage to avoid overages and unexpected fees. A SaaS agreement should define those thresholds and explicitly detail the fees for exceeding them. Depending on the SaaS tool, your line items might include the following:
- Feature, product, or service name
- Quantity of licenses
- Unit price per license
- Total value of all line items
- Free licenses and/or discounted licenses
- License allocation
- Platform details
- Professional services
- SaaS provider contacts
12. Subscription Term, Termination, and Exit Strategies
A clear termination policy is vital to any SaaS agreement, ensuring both parties understand the terms for ending the subscription. Organizations may face unexpected penalties, disruptions, or complications in transitioning to a new provider without a well-defined policy. Including exit strategies and termination clauses in your SaaS checklist helps protect your organization’s interests and provides a roadmap for navigating the end of a contract.
Termination clauses typically cover scenarios such as early cancellation, contract breaches, or the subscription term’s end. Key elements to look for include:
- Notice Period Requirements: The amount of time required to provide written notice before termination, often tied to renewal deadlines.
- Penalties for Early Termination: Any fees or forfeited funds associated with ending the contract before its expiration.
- Data Transition and Retention Policies: Clear instructions on how data will be handed over, deleted, or stored post-termination to prevent data loss or breaches.
- Exit Support: Provisions for assistance in migrating data or systems to a new provider, ensuring a smooth transition.
A robust termination policy doesn’t just safeguard your organization—it also gives you flexibility to make strategic changes when needed. Reviewing these details ensures you’re prepared to handle the end of a SaaS agreement while maintaining continuity and minimizing risks.
13. Access Rights and User Management
Defining access rights and managing users is a critical aspect of any SaaS agreement. Clear terms ensure that only authorized individuals can access the platform while preventing misuse or over-allocation of licenses.
Key considerations include:
- User Roles and Permissions: Outlining different levels of access based on job responsibilities to maintain data security and operational efficiency.
- Maximum Number of Users: Ensuring the agreement specifies limits on the number of users and provides options for scaling as your organization grows.
- Account Management Policies: Defining how user accounts are created, modified, or deactivated, particularly during personnel changes.
Including these details in your SaaS agreement prevents confusion, minimizes security risks, and helps optimize license usage across the organization.
14. Customer Support and Services
Effective customer support is a vital component of any SaaS agreement. Clear terms ensure your organization knows what level of assistance to expect and how to access it when needed. For instance, what are the hours of operation, and is support offered 24/7 or during specific time zones?
What are the methods for accessing assistance, such as email, phone, live chat, or dedicated account managers? By outlining the agreement’s customer support and service terms, your organization can avoid delays and ensure a seamless experience when addressing technical or operational concerns.
15. License Scope
Understanding how a SaaS license can be used is essential for staying compliant and maximizing value. Key factors include usage limits, such as the number of users or devices allowed, geographic restrictions, and permitted activities. These terms ensure the software is used appropriately and within the agreed boundaries, preventing unexpected penalties or access issues.
16. Warranties
SaaS agreements often include warranties to guarantee the performance and reliability of the service. Common warranties cover uptime, data security, and compliance with regulations. Reviewing these terms ensures accountability and provides recourse if the service fails to meet expectations.
17. Limitations on Liability
Liability clauses define the extent to which a SaaS provider is responsible for damages or losses resulting from their service. These terms often limit the provider’s liability to the subscription fees paid and exclude responsibility for indirect or consequential damages.
Understanding these limitations helps your organization assess risks and determine whether additional protections, such as insurance or contract amendments, are necessary.
18. Variables and Extra Charges
SaaS agreements may include variables or additional charges that affect your total costs, such as fees for exceeding usage limits, premium support services, or enhanced security features. Carefully reviewing these terms helps avoid unexpected expenses and ensures alignment with your budget.
19. Intellectual Property Rights and Data Ownership
Understanding intellectual property rights (IPR) and data ownership clauses is critical in any SaaS agreement. These clauses specify who owns the software, customizations, and the data generated or stored within the platform. Clear definitions protect your organization’s interests and prevent disputes over access or usage.
20. Key Legal Policies
SaaS agreements often incorporate several legal policies that define acceptable use and outline vendor and customer responsibilities:
- Terms of Service (ToS): Details of acceptable use and the boundaries of the service.
- End User Licensing Agreement (EULA): Specifies user rights and safeguards the vendor’s intellectual property.
- Privacy Policy: Declares how user data is protected, enhancing transparency and trust.
Including these policies ensures clarity and compliance with legal and ethical standards.
21. Indemnities
Indemnity clauses outline how the vendor or customer will cover losses related to breaches, intellectual property disputes, or data issues. Reviewing these terms helps ensure accountability and mitigates potential risks for both parties.
22. Vendor Insurance Requirements
Some SaaS agreements include provisions requiring vendors to maintain liability insurance, such as cyber liability or professional indemnity coverage. These clauses add an extra layer of protection, ensuring vendors are equipped to handle potential claims or damages.
23. Publicity Rights
Publicity clauses specify whether the vendor can use your organization’s name or logo in marketing materials. If you prefer to restrict this use, it’s essential to address it explicitly in the agreement.
Ensure Visibility of SaaS Agreement Details
Enhanced visibility into SaaS agreements offers significant benefits, including reducing software costs, eliminating redundancies, and allocating resources more effectively. The first step is identifying and organizing key details in your contracts, which sets the foundation for a smarter and more strategic approach to SaaS management.
Zylo provides a comprehensive platform for tracking spend, usage metrics, and contract terms. Its contract concierge service further simplifies the process by ensuring all critical details are accurately recorded and easily accessible within your Zylo account. Request a demo today to understand how identifying and managing critical SaaS agreement details enables modernized software management.