10/24/2024
Table of Contents
Updated on February 20, 2026 with new data.
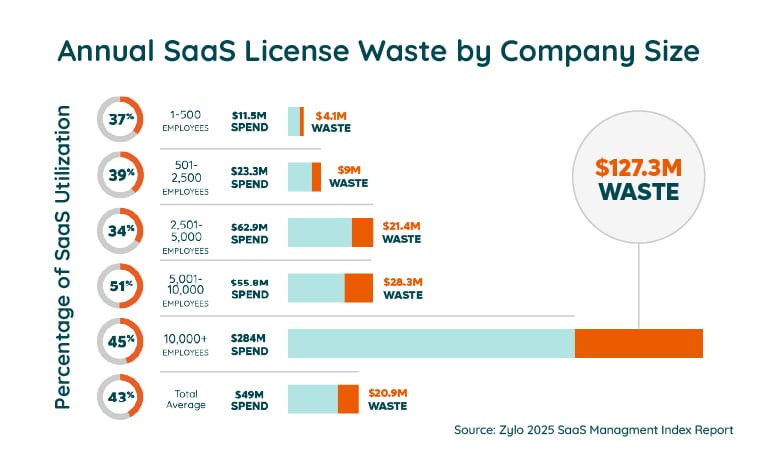
According to Zylo’s 2026 SaaS Management Index, 43% of enterprise software licenses go unused—costing companies an average of $80.6M annually. That’s the cost of poor software license management. For more industry-wide numbers on SaaS usage and spend, check out our 2025 SaaS Statistics report. This guide shows you how to take control, cut waste, and stay compliant.
What Is Software License Management?
Software license management (SLM) is the process of tracking and managing all software licenses across your organization—on-premises and SaaS—to reduce costs, ensure compliance, and improve security.
Key goals of a license management system:
- Optimize software investments
- Ensure compliance with license agreements
- Align software use with business needs and policies
Hear more on software license management in terms of SaaS from Zylo co-founder Ben Pippenger on the SaaSMe Anything podcast.
In this short overview, Ben Pippenger explains the software license management process: centralized inventory, usage audits, compliance checks, and rightsizing to cut SaaS waste.
What Are the Best Tips for Software License Management?
The best tips for software license management include tracking all licenses in one place, auditing usage regularly, cutting unused licenses, ensuring compliance with vendor terms, and choosing tools that automate reporting. These steps reduce costs, improve visibility, and prevent overspending on software.
- Track all software licenses centrally
- Audit usage and remove unused licenses
- Stay compliant with vendor agreements
- Automate reporting with management tools
- Optimize costs by consolidating licenses
How Do AI Tools Affect Software License Management?
AI tools impact software license management by adding new costs, usage models, and compliance requirements that must be tracked alongside traditional software.
Key ways AI changes license management:
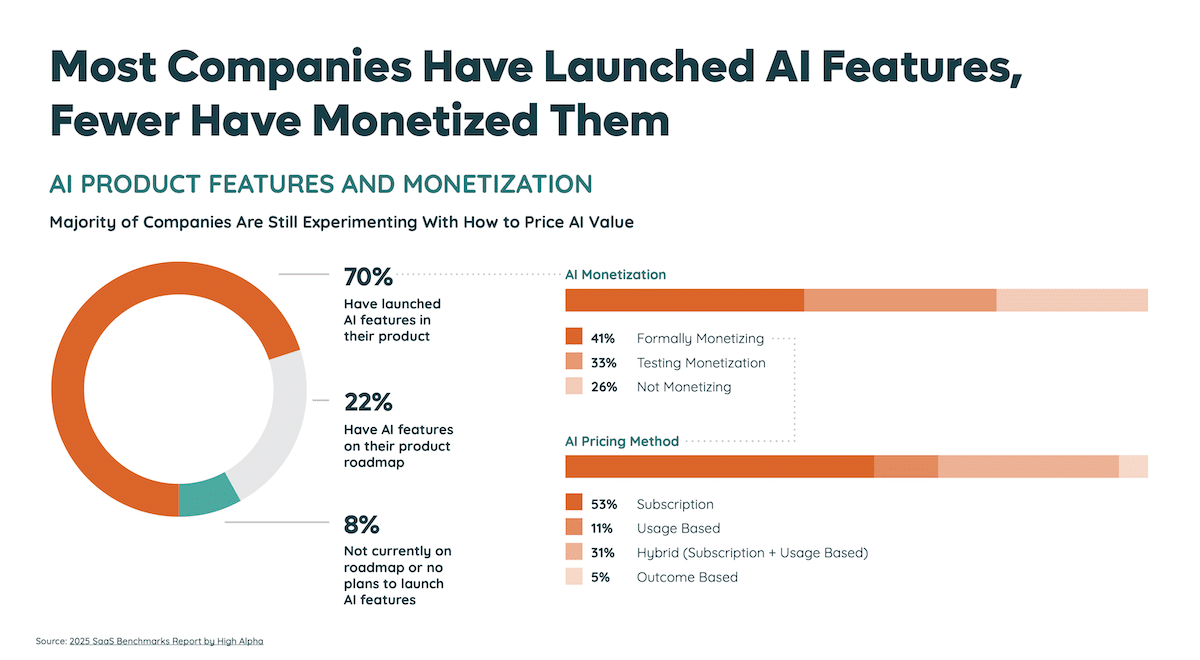
- New Pricing Models – Many AI tools use consumption-based billing (tokens, queries, API calls) instead of flat fees, requiring closer monitoring. The 2026 SaaS Benchmarks Report by High Alpha found that 41% of SaaS companies price by usage or hybrid (a combination of usage and subscription).
- Bundled Features – Vendors are embedding AI into existing SaaS platforms, sometimes raising prices or creating hidden licensing complexity.
- Evolving Terms – AI licensing agreements change frequently, making compliance tracking more important than ever.
- Rising Costs – Without oversight, AI subscriptions can quickly become a major driver of software overspend.
💡 Want a deeper dive? Explore our breakdown of AI costs for businesses in 2025.
Types of Software Licenses in Application License Management
Understanding software license types is critical to effective software license management and optimizing your software license management process.
Common license types:
- Proprietary – Restricted use, no modification
- Freeware/Shareware – Free or trial use, limited rights
- Open Source/Copyleft – Modifiable; Copyleft keeps derivatives open
- Subscription-Based – Monthly/annual SaaS payments
- Concurrent User – Limit on simultaneous users
- Public Domain – No restrictions
- LGPL – Mix open source with proprietary code
Proprietary Licenses
A proprietary license grants the user rights to use the software but restricts modification, distribution, and access to the source code. The software remains the vendor’s intellectual property, and users must comply with the specific terms set by the license.
Limited Use Licenses (Freeware & Shareware)
- Freeware: This type of software is available for use at no cost but typically restricts modification, distribution, or commercial use. Unlike open-source software, freeware often keeps the source code hidden from users.
- Shareware: Shareware is distributed on a trial basis, allowing users to test the software before purchasing a full license. After the trial, continued use generally requires payment, with restrictions on modification and redistribution.
Open Source and Copyleft Licenses
- Open Source: Open-source licenses allow users to modify, distribute, and use the software freely, as long as they comply with specific terms, such as attributing the original creators.
- Copyleft: Copyleft licenses, such as the GNU General Public License (GPL), require that any modifications made to the software be distributed under the same licensing terms, ensuring that derivative works remain open-source.
Subscription-Based and Concurrent User Licenses
- Subscription-Based License: This model provides access to software on a recurring payment basis, typically monthly or annually. It is common for SaaS platforms, where businesses pay for continuous access and updates.
- Concurrent User License: These licenses allow a specific number of users to access the software simultaneously, maximizing cost efficiency by limiting active users rather than total employees.
Public Domain License
A public domain license allows anyone to modify, distribute, or sell the software without restrictions, as intellectual property laws like copyrights or patents do not protect it.
Lesser General Public License (LGPL)
The LGPL is a more flexible version of the GPL. It allows developers to integrate LGPL-licensed components into proprietary applications as long as modifications to the LGPL-licensed parts remain open-source.
The IT Leader’s Guide to Software License Management
Learn MoreWhy Software License Management Compliance Matters
Maintaining compliance with license requirements—through robust software license management processes and tools—prevents legal, financial, and operational risks.
Compliance Standards in Software License Management
- SOC 2 (crucial for SaaS license management)
- NIST 800-53 (cybersecurity controls)
- ISO/IEC 27001 (secure management of software licenses and data)
SOC 2
Focused on data security, availability, and confidentiality, SOC 2 is especially crucial for SaaS and cloud-based software. It ensures that organizations manage data responsibly and protect against breaches or service interruptions.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (NIST 800-53)
NIST offers security controls and best practices for protecting information systems. By following these guidelines, organizations reduce the risk of data breaches and ensure that software license usage meets high-security standards.
ISO/IEC 27001
An international standard for information security management systems (ISMS), ISO/IEC 27001 ensures that software and systems are secured, helping organizations follow best practices in protecting their data and licenses.
Benefits of Software License Management Solutions
The right software license management solutions bring clarity and control to complex software environments.
With a License Management Software Solution, You Can:
- Cut waste: eliminate unused licenses and renewals
- Avoid audits: stay compliant with vendors
- Protect data: revoke access quickly during offboarding
- Make decisions: use reports to guide renewals and savings
Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings
Gaining visibility into software usage and licenses can help businesses eliminate redundant licenses and underutilized software. This data helps identify opportunities to rightsize license allocations, preventing unnecessary spending. Additionally, SLM enables companies to streamline processes, avoid costly audits, and stay compliant with vendor agreements.
Guide to Managing SaaS Costs
Learn MoreCompliance and Cybersecurity
SLM ensures that businesses remain compliant with licensing terms, avoiding potential fines or penalties. It ensures that businesses only use what they pay for, and pay for what they use. With improved visibility, businesses can align purchases with actual business needs. They can also mitigate security risks by ensuring that licenses are properly managed, especially when employees leave, or licenses are no longer needed.
Reporting and Accountability
With detailed reporting capabilities, businesses can track software usage and license allocation in real time. By monitoring key software license management initiatives like downgrading, deprovisioning, and rightsizing, companies can demonstrate the value of SLM. This transparency improves decision-making, helps justify software investments, and creates accountability across the organization.
Consequences of Poor Software License Management
Without a solid software license management system, risks grow fast. Neglecting license management leads to a range of financial and operational problems:
- Wasted spend: Unused software licenses (shelfware) drain budgets—Zylo’s 2026 Enterprise SaaS Management Report quantifies this at up to $80.6M wasted each year for large enterprises. Read more about SaaS shelfware risk
- License overages: Exceeding terms increases costs, causes compliance issues
- Security gaps: Unmanaged licenses expose your organization to data risk
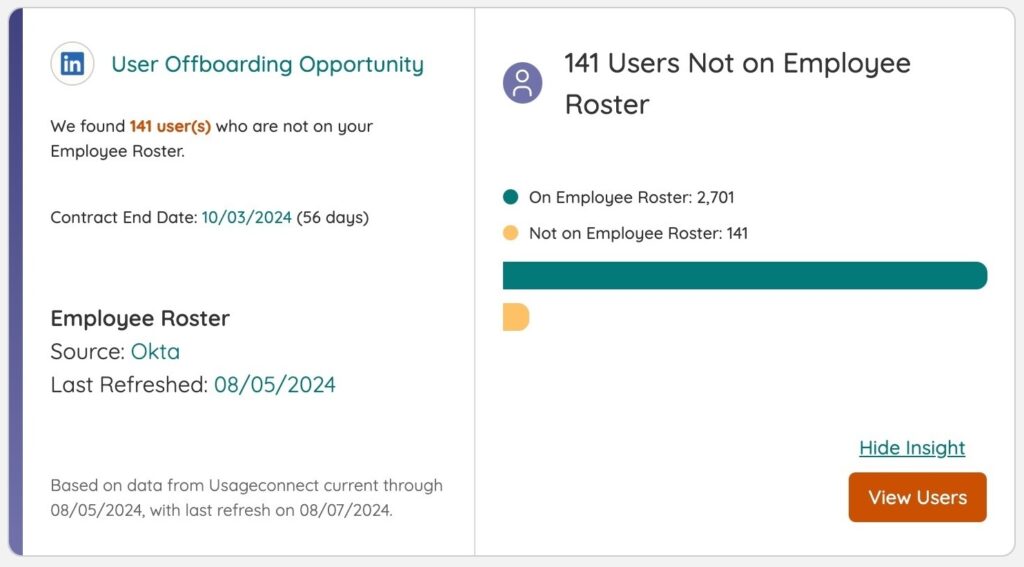
- Cost allocation problems: Without accurate data, showbacks and chargebacks are unreliable. Get user offboarding insight in Zylo
Underutilized Software
Many businesses purchase more software licenses than they use, leading to wasted resources. Known as shelfware, these unused licenses result in significant financial losses that could have been avoided with better oversight. Additionally, lacking usage data can lead to poor renewal decisions, as organizations fail to secure the correct types or amounts of licenses to match their business needs.
License Overages and Compliance Issues
Overusing software licenses beyond what has been purchased can result in costly overages. These violations can lead to fines, legal action, and tarnished vendor relationships. By tracking licenses effectively, businesses can avoid these compliance issues.
Data Security Risks
Businesses risk unauthorized access to sensitive data when licenses aren’t properly deprovisioned after an employee leaves. This presents a serious security vulnerability, as former employees or third parties may access company systems without permission.
Challenges with Showbacks and Chargebacks
It’s challenging to allocate costs accurately to departments without accurate usage data. This lack of visibility hinders showback or chargeback processes, as license usage is a critical data point for calculating department-specific expenses and ensuring fair resource distribution.
How to Manage Software Licenses Effectively
Beyond compliance, managing software licenses plays a key role in reducing costs and aligning IT decisions with business goals. Effective license management controls costs, boosts efficiency, and ensures alignment between IT and business objectives.
- Enterprise software license management: Monitor and reclaim licenses, ensuring resources match need
- Cost allocation/chargeback: Track spend by department for accountability Learn about chargebacks/showbacks
- Renewals: Leverage usage data to renew the right licenses and avoid waste Explore SaaS license management and renewal best practices
Enterprise Software License Management
Enterprise software license management involves tracking software usage, identifying underutilized licenses, and reallocating resources to optimize value. By analyzing usage data, IT and SAM teams can reduce waste and ensure licenses are properly deployed where they’re needed. This is especially critical with apps with complex licensing structures and multi-org instances, like Salesforce licenses.
This approach also ensures compliance with vendor agreements, minimizing the risk of penalties from audits. Ultimately, it maximizes the return on your software investments while reducing operational costs.
Cost Allocation
Using cost allocation methods like showbacks and chargebacks promote accountability by assigning software costs to individual departments. Showbacks provide transparency, while chargebacks require departments to cover their software expenses. This practice encourages departments to be mindful of their software usage, helping reduce unnecessary costs and driving more efficient budget management.
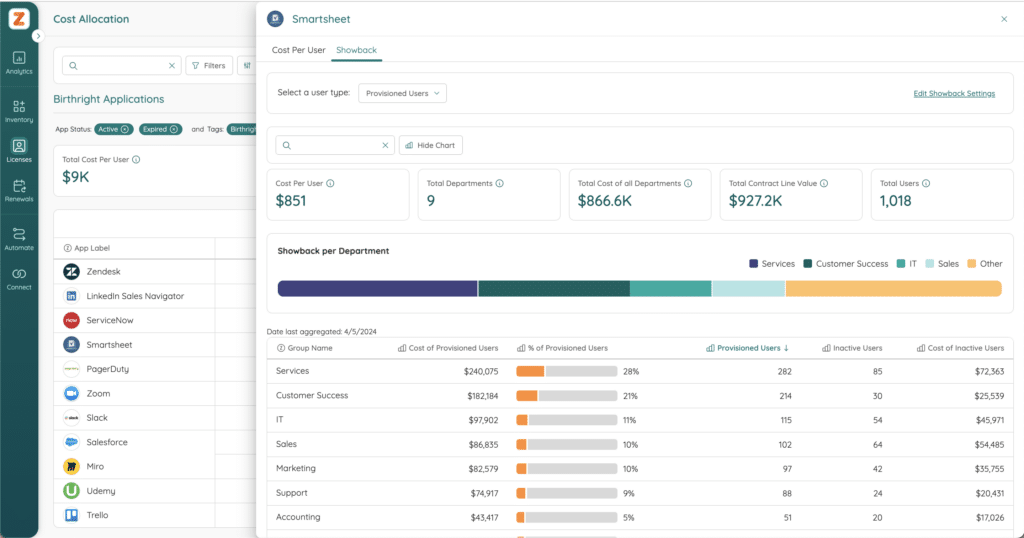
Renewal Decisions
License renewals are another key aspect of license management. IT and SAM teams, working with Procurement, analyze usage data to determine the right number of licenses to renew. This data-driven approach ensures companies only pay for what they actually use, saving money. Collaboration between IT, SAM, and Procurement ensures that renewal decisions are informed and cost-effective, optimizing software investments.
App-Specific License Management
Check out these resources more nuanced license management guidance on specific applications:
- Salesforce
- Microsoft 365
- Zoom
- Adobe
- Slack
- DocuSign
- Atlassian
- Smartsheet
- Miro
- GitHub
- Google Workspace
- Zendesk
Common Software License Management Challenges
Managing software licenses effectively requires full visibility and open communication across departments. Without these, businesses face several key challenges:
- Shadow IT and unauthorized software use
- Maintaining up-to-date license records
- Lack of visibility
- Departmental silos
- Outdated license records
- Automated renewals
- The cost of software licenses
- Change management
- Automatic renewals: involuntary renewals can inflate costs
- Duplicate purchases: multiple departments buying overlapping software
Shadow IT and Unauthorized Software Use
Shadow IT—when employees use unapproved software—creates visibility issues, security risks, and compliance challenges. Our research shows that nearly 45% of SaaS apps in use are unauthorized, underscoring the need for better software management. Without visibility, businesses face overspending and compliance risks. A robust software management solution helps regain control, reduce waste, and improve security.
Maintaining Up-To-Date License Records
Accurate license records are key to making informed decisions on renewals, reclamations, or downgrades. Outdated data can lead to overspending or compliance issues. Legacy tools and spreadsheets often fail to keep records current. Modern management platforms provide real-time data, making optimizing costs and staying compliant easier.
Lack of Visibility
Businesses often rely on outdated tracking methods, like spreadsheets, that don’t provide a complete picture of license usage. This can lead to over-purchasing, noncompliance, or missing opportunities to reclaim unused licenses.
Departmental Silos
When IT, Procurement, and other teams fail to communicate, license decisions may be made without understanding the broader implications that affect hundreds, even thousands, of employees. This disjointed approach results in missed opportunities for cost savings and inefficient license management.
Sam Chung, Chief Transformation Officer at Salesforce, recommends using what he calls “business intimacy” to overcome departmental silos. With this concept of collaboration, it becomes easier for IT, Procurement, and Finance to coordinate license optimization.
Outdated License Records
Keeping license records up to date is critical for making informed renewal and reclamation decisions. Legacy tools often fail to track software usage accurately, leading to wasted licenses or compliance issues.
Automated Renewals
Automatic renewals can prevent businesses from taking the time to assess licensing needs and make necessary changes. Without time to review licenses against current business requirements, companies may renew subscriptions they no longer need.
The Cost of Software Licenses
Duplicate licenses or subscriptions can lead to unnecessary costs, diluting purchasing power and leading organizations to pay for software they don’t actually need.
Change Management
Effective change management is essential when implementing new license workflows, such as reclamations or downgrades. Clear communication and cross-departmental buy-in are necessary to reduce resistance to new processes.
Features to Look for in License Management Software
Top software license management solutions and license management software platforms should offer:
- Centralized inventory dashboards
- Renewal alerts
- Robust integrations
- Compliance tracking
- Security monitoring
- Cost optimization
- Automated Reports
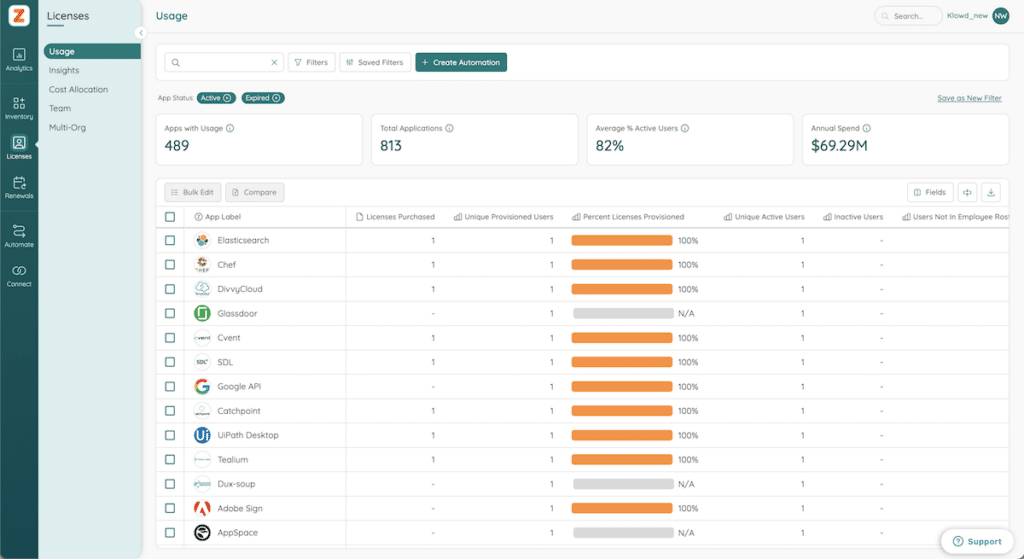
Real-Time Visibility and Tracking of Your Software License Inventory
Knowing what software you have is the first step to effective license management. A centralized software license inventory provides businesses with real-time data on license usage, helping prevent overages or underutilization.
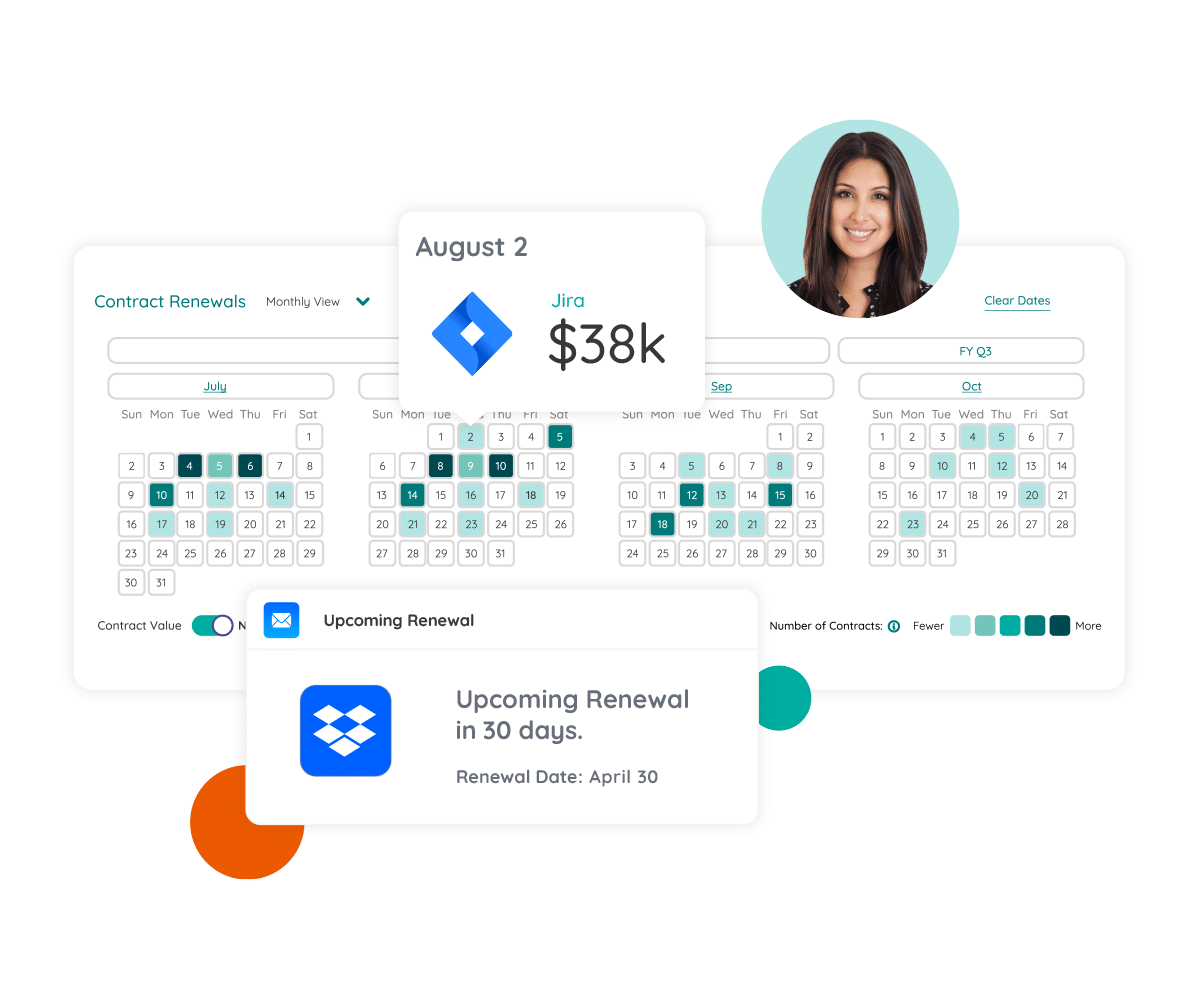
Streamlined License Renewals
Centralizing renewal and contract data gives you clear visibility into upcoming renewals, helping you rightsize licenses and avoid unnecessary costs.
Data Integration
Quality integrations with other platforms ensure that data about users and software licenses is accurate and up to date. This reduces redundancies and allows businesses to monitor license usage seamlessly.

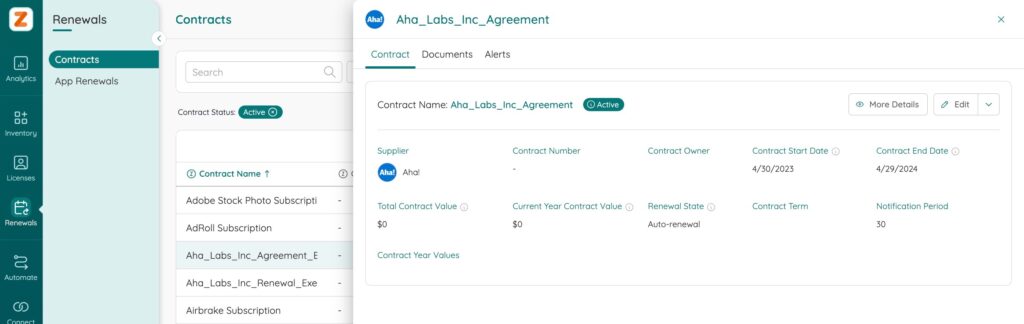
Legal and Contract Compliance
License compliance ensures your business stays within contract terms and avoids penalties. Automated tools provide insights to spot potential overages or underutilized licenses, helping reduce waste and manage costs effectively.
Improve Cybersecurity
Identifying apps with poor risk scores is critical to strengthening your security posture. Effective software management highlights these risks, helping mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Cost Optimization
Software management tools provide visibility into spend per application and license, offering cost-per-user metrics that help optimize expenses and reduce waste.
Automated Reports
By automatically generating and distributing reports, businesses can maintain transparency and hold departments accountable for their software usage. These reports provide valuable insights into compliance and cost-saving opportunities.
2024 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for SaaS Management Platforms
Learn MoreSoftware License Management Best Practices
To get full ROI, your software license management process must be proactive, connected, and data-led.
How to manage software licenses with maximum ROI:
- Monitor usage continuously
- Leverage data for smarter renewals
- Train employees on software policies
- Centralize your license inventory
- Sync with procurement
- Update records regularly
Regular Compliance Checks and Continuous Monitoring
For on-premises software, periodic audits help ensure compliance, but they often lack the real-time visibility needed for dynamic license management. In contrast, managing SaaS licenses involves continuous discovery, with automated alerts for capacity limits and renewal reminders. This ongoing approach enables proactive adjustments and supports regular security reviews.
Vendor Relationship Management
Accurate usage data allows for better negotiations with software vendors. Businesses can renegotiate contracts to eliminate unused licenses and optimize their software spending.
Training and Awareness
Educating staff about the importance of license management improves efficiency and reduces waste. When employees understand license workflows, like reclamation or downgrading, they are more likely to follow the processes that benefit the business.
Partner with Procurement to Streamline Renewals
Collaborating with your Procurement team is essential for optimizing software renewals. By bringing forward accurate license data, Procurement can renew the correct number of licenses based on actual usage. This partnership ensures you aren’t overpaying for unused licenses or scrambling for more as needs increase, ultimately driving cost savings and operational efficiency.
Use Software License Management Solutions
Managing both on-premises software and SaaS applications requires specialized tools for each. These tools give you a centralized way to track and manage licenses, whether for legacy systems or cloud-based software. An SMP helps ensure compliance, reduce spend, and keep your entire software ecosystem running smoothly.
Keep Your Licensing Data Current with Continuous Updates
Software license management isn’t a one-time task. Ongoing discovery and regular data syncs are crucial to keeping your system of record up to date. Continuous license usage tracking ensures you stay compliant, avoid unnecessary renewals, and adapt your strategy based on current needs. Always-on discovery helps ensure that your licensing data is accurate and actionable.
The No-BS SaaS Management Playbook
Learn MoreSoftware License Management FAQs
These frequently asked questions (FAQs) offer concise answers that help clarify key aspects of software license management (SLM) and address common queries.
What is the software license management process?
The software license management process is the method organizations use to track, control, and optimize software licenses for compliance and cost savings.
Key steps in the process include:
- Inventory: Identify all software currently in use and the licenses tied to each product.
- Tracking: Monitor license usage in real time to spot underutilized or unused software.
- Compliance: Compare actual usage against vendor terms to avoid audits and penalties.
- Optimization: Reassign or reduce licenses where possible to cut unnecessary costs.
- Renewal Management: Plan ahead for contract renewals to negotiate better terms.
Why it matters:
- Prevents unexpected costs from non-compliance.
- Reduces waste by eliminating unused licenses.
- Improves budgeting and forecasting for SaaS and software spend.
What are the four types of software licenses?
The four main types of software licenses are proprietary, open-source, freeware, and shareware:
- Proprietary License – The vendor owns the software, and users must follow strict terms. Typically no modifications or redistribution are allowed.
- Open-Source License – The source code is available to the public, allowing modification and redistribution. Examples: MIT, Apache, GNU GPL.
- Freeware License – Software is provided at no cost, but usually with limited rights (cannot modify or resell).
- Shareware License – Software is distributed for free on a trial basis, with payment required for continued or full-featured use.
Why this matters: Understanding license types helps organizations stay compliant, avoid legal risks, and choose the right model for cost and flexibility.
What are three common software licenses?
The three most common types of software licenses are proprietary, open-source, and freeware.
- Proprietary License – Controlled entirely by the vendor; users can’t modify or redistribute the software.
- Open-Source License – Source code is available for anyone to view, modify, and share under license terms (e.g., MIT, GPL).
- Freeware License – Software is free to use but usually with restrictions, such as no modifications or resale.
Why it matters: These license types cover the majority of business and personal software, making it critical to understand their limitations and rights.
Are software licenses capitalized or expensed?
Software licenses can be either capitalized or expensed depending on the type and term of the license.
Perpetual Licenses (Capitalized):
- Treated as an asset because the organization owns the software indefinitely.
- Costs are capitalized and then amortized over the useful life of the software.
Subscription or Term-Based Licenses (Expensed):
- Treated as an operating expense since the company is paying for temporary access.
- Costs are expensed as incurred, usually monthly or annually.
💡 Rule of thumb: If you own it, capitalize it. If you rent it, expense it.
Why it matters: Correct classification ensures accurate financial reporting, better budgeting, and compliance with accounting standards (GAAP, IFRS).
What is license management software?
License management software tracks, optimizes, and automates compliance for all your business software licenses.
What is license management?
License management is the process of organizing, tracking, and optimizing the use of software licenses across your organization.
What happens if you don’t manage software licenses?
Unmanaged licenses lead to wasted spend, compliance penalties, and security risks.
How does a license management system work?
A license management system consolidates your software license inventory, monitors usage, automates renewals, and provides compliance and optimization reporting.
How do enterprise companies manage software licenses?
Leading organizations use enterprise software license management tools and solutions like Zylo’s SaaS Management platform, ensuring accurate tracking, centralized renewals, and actionable spend insights.
How can I improve my software license management process?
Follow software license management best practices: use a license management system, educate employees, keep data current, and foster cross-departmental transparency.
Enterprise Software License Management Solutions by Zylo
Zylo’s software license management solutions empower organizations to manage software licenses at scale, optimize spend, and maintain compliance.
This article is brought to you by Zylo – the enterprise leader in SaaS Management. Companies such as AbbVie, Adobe, Atlassian, Intuit, Salesforce, and Yahoo leverage Zylo’s AI-powered platform and unparalleled professional services to fuel centralized SaaS inventory, license optimization, and renewal management.
Ready to improve your software license management process? Contact Zylo for a demo and take control of your IT license management.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Ben Pippenger
Ben Pippenger is Staff Product Manager and Co-Founder of Zylo, where he helps enterprises maximize the value of their SaaS investments. With more than 20 years of experience in B2B software, Ben is a recognized thought leader in SaaS Management, license optimization, and IT strategy. Before founding Zylo, he held product and account leadership roles at Salesforce and ExactTarget. A self-proclaimed SaaS geek, Ben regularly speaks on topics like shadow IT, SaaS ROI, and software lifecycle management.