Table of Contents
Updated December 9, 2025 – Updated best practices and expanded insights on Software Asset Lifecycle Management.
Software Asset Management is essential for organizations seeking to control costs, reduce risk, and derive greater value from their software investments. As companies expand, managing software across its entire lifecycle—from procurement through retirement—becomes increasingly complex.
A well-structured SAM strategy strengthens compliance, improves security, and provides the visibility needed to make smarter decisions. This guide covers the core benefits, best practices, and practical steps that help you manage software assets efficiently and maximize their impact across your organization.
What Is Software Asset Management (SAM)?
Software Asset Management (SAM) refers to the processes and tools used to manage, control, and protect on-premises software assets and SaaS throughout their life cycle. It helps organizations:
- Use licenses efficiently
- Maintain compliance with licensing agreements
- Reduce unnecessary spending
- Limit security risks
- Streamline IT operations by bringing order and visibility to an increasingly complex software environment
What Is an Example of a Software Asset?
Software assets include on-premises applications and subscription-based tools such as SaaS and cloud solutions. On-premises software runs on internal servers, while SaaS and cloud tools are hosted externally and purchased through recurring subscriptions. SAM helps organizations manage usage, renewals, and compliance across all these environments.
Software Asset Management vs Software License Management (SLM)
SAM and software license management (SLM) are related but not identical. SAM takes a wider view of how software is used and governed across the organization, while SLM focuses more narrowly on licensing rules and compliance.
SAM typically includes:
- License positioning and usage analysis across the broader application portfolio
- Visibility into ownership, usage patterns, and optimization opportunities
- Governance activities that help reduce waste and strengthen decision-making
- Support for compliance, renewal planning, and portfolio-level insights
- Coordination with IT operations, even if tasks like onboarding/offboarding sit elsewhere
SLM specifically focuses on:
- Tracking entitlements and understanding exactly what has been purchased
- Ensuring compliance with vendor license terms and contractual requirements
- Monitoring license consumption to avoid overuse or underuse
- Managing renewal obligations tied directly to licensing rules
- Providing precise compliance data used by SAM, IT, procurement, and audit teams
The Relationship Between SAM and IT Asset Management (ITAM)
Software Asset Management is part of the broader practice of IT asset management (ITAM), which covers hardware, software, and supporting data. ITAM provides an organization-wide framework for managing all technology assets, while SAM zeroes in on software-specific visibility, compliance, and optimization. Together, they ensure that technology investments are aligned, controlled, and cost-effective.
How the two disciplines differ in scope:
- ITAM governs hardware, software, and data across their full lifecycle
- SAM concentrates on software usage, licensing, and optimization
- ITAM sets the framework; SAM executes software-specific oversight within it
4 Need-to-Know SaaS Stats for Software Asset Management
Learn MoreWhat Is Software Asset Lifecycle Management?
Software asset lifecycle management refers to the full process of governing software from evaluation through retirement:
- Evaluation and selection of applications
- Procurement, contracting, and licensing
- Deployment and configuration
- Ongoing monitoring, maintenance, and optimization
- Renewal planning or retirement of applications
Effective lifecycle management provides:
- A clear understanding of what the organization owns and how it is used
- Stronger budgeting and renewal planning
- Lower compliance and audit risk
- Reduced waste from unused or duplicate subscriptions
- Better decision-making through complete lifecycle visibility
How Software Asset Management Is Evolving in 2026
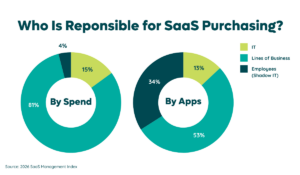
Software Asset Management is shifting rapidly as organizations adopt more SaaS, expand hybrid work, and manage larger, more decentralized portfolios. Business units now drive over 50% of software purchases, and IT owns just 26.1% of spend.
Several factors are driving this change, including:
- The growth of usage-based pricing models
- Faster procurement cycles across business units
- The need for real-time visibility into ownership, usage, and spend
- Increasing pressure to identify waste and manage renewals proactively
- Automated discovery to keep pace with new tools entering the environment
- Predictive forecasting to anticipate renewals and budget needs
- Intelligent recommendations that highlight waste, rightsizing opportunities, and compliance risks
- Reduced manual work through automated analysis and data normalization
As software environments continue to grow in size and complexity, these AI-driven capabilities are becoming essential for maintaining efficiency, strengthening governance, and keeping software portfolios under control.
The Benefits and Importance of Software Asset Management
SAM delivers measurable advantages that help organizations control software costs, strengthen governance, and improve operational efficiency across increasingly complex environments. These include:
- Cost savings
- Compliance and governance
- Risk management and mitigation
- Improved operational efficiency
- Vendor relationship management
- More efficient decision-making
- Monitoring and usage tracking
- Improved security
- Audit readiness
- Transparency and data visibility
- Strategic planning and lifecycle management
Cost Savings
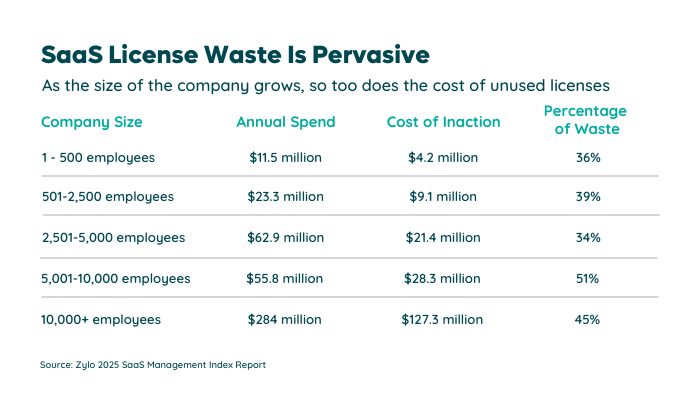
According to the 2025 SaaS Management Index, SaaS spending increased 9.3% year over year, averaging $49M annual. On top of that, vendor prices are rising. SAM helps reduce overages and unexpected fees by optimizing license usage, eliminating waste, and rightsizing contracts at renewal.
With average SaaS utilization at just 47.3% and unused licenses driving roughly $21M in annual waste for the average organization, ongoing optimization ensures companies only pay for what they actually need.
Compliance and Governance
Effective SAM helps ensure companies use what they pay for and pay for what they use. It also minimizes exposure to non-compliance penalties and reduces shadow IT risk—an important factor as business units now account for 70% of SaaS spend. Strong governance policies supported by SAM create consistency across software purchasing and usage.
Risk Management and Mitigation
SAM plays a supporting role in reducing operational and security risks by maintaining accurate software inventories and providing visibility into what is deployed across the organization. These insights help Security and InfoSec teams identify outdated, unapproved, or unmanaged applications that may introduce vulnerabilities. By partnering closely with these teams, SAM ensures they have the data needed to assess risk, enforce policies, and respond to potential issues more effectively.
Improved Operational Efficiency
Zylo research found that over half (51.7%) of IT leaders say software licensing models are too complex to manage. By streamlining license administration and automating repetitive tasks, SAM frees IT and Procurement teams to focus on higher-value initiatives. Automation also shortens renewal cycles and speeds up decision-making, improving overall productivity.
Vendor Relationship Management
SAM provides detailed insights into usage patterns and contract performance, enabling Procurement teams to negotiate renewals with accurate, data-backed intelligence. As vendors introduce new AI features and more complex pricing models, having this visibility helps prevent overspending and supports stronger, more balanced vendor relationships.
More Efficient Decision Making
With SAM, you gain a trusted, centralized source of truth for your software usage, entitlements, cost, and ownership. Instead of relying on assumptions, scattered spreadsheets, or competing opinions across departments, you can make decisions grounded in clear, reliable data. This transparency empowers you to identify:
- Where consolidation makes sense
- What licenses need to be rightsized
- Which applications no longer deliver value
When you have consistent insights at your fingertips, your software decisions become faster, more strategic, and aligned with your long-term business goals.
Monitoring & Usage Tracking
SAM offers continuous visibility into how tools are used across the business. This ability helps organizations:
- Maximize adoption
- Identify underutilized licenses
- Make informed choices before renewals
Improved Security
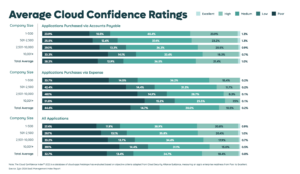
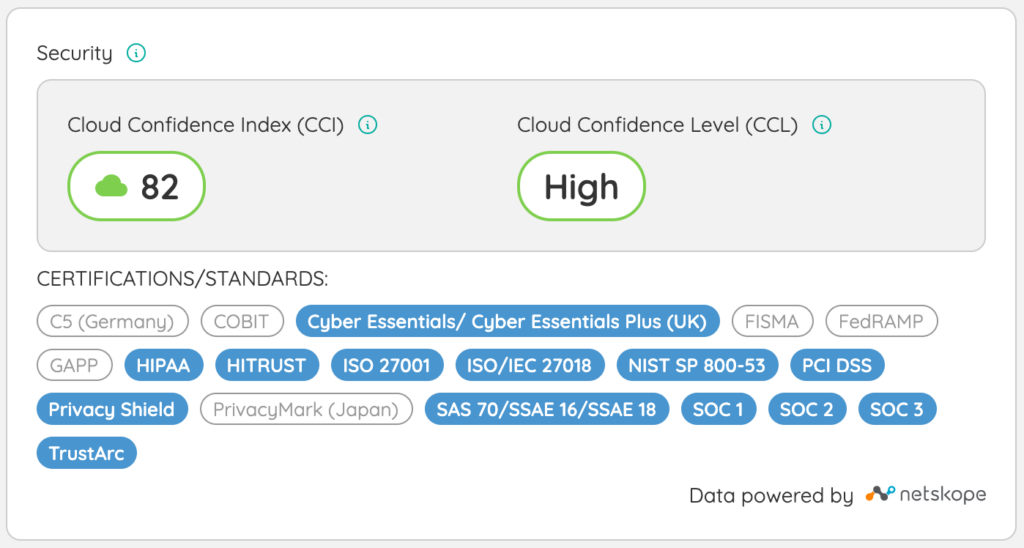
Sixty-one percent of applications are rated as Poor or Low on the Cloud Confidence Index, and only 21.4% of apps sit behind SSO. With SAM, you can start closing those gaps by giving Security and InfoSec centralized visibility into your software environment. This visibility makes it easier to
- Identify unmanaged tools
- Tighten user access
- Bring more of your environment under proper governance
Audit Readiness
SAM helps you stay prepared for vendor audits by giving you accurate, up-to-date records of your licenses and usage. When you can clearly see what you’ve purchased and how it’s being consumed, you reduce the chance of unexpected findings, surprise penalties, or unintentional overuse. With cleaner data and fewer gaps, you can approach audits with confidence instead of stress.
Transparency & Data Visibility
With centralized software data, you get a clear, trusted view of how your applications are being used and what they cost. This visibility helps you:
- Forecast spend more accurately
- Build realistic budgets
- Understand where every dollar goes
Instead of chasing information across teams or relying on estimates, you can make decisions grounded in reliable insights that everyone aligns around.
Strategic Planning & Lifecycle Management
By managing your software from acquisition through retirement, SAM gives you insights needed to
- Plan upgrades
- Streamline software transitions
- Ensure each tool continues to serve the business well
When you can see where an application is in its lifecycle, you’re better equipped to determine whether to maintain it, replace it, or retire it. These ongoing insights help you keep your portfolio healthy and optimized as your organization grows.
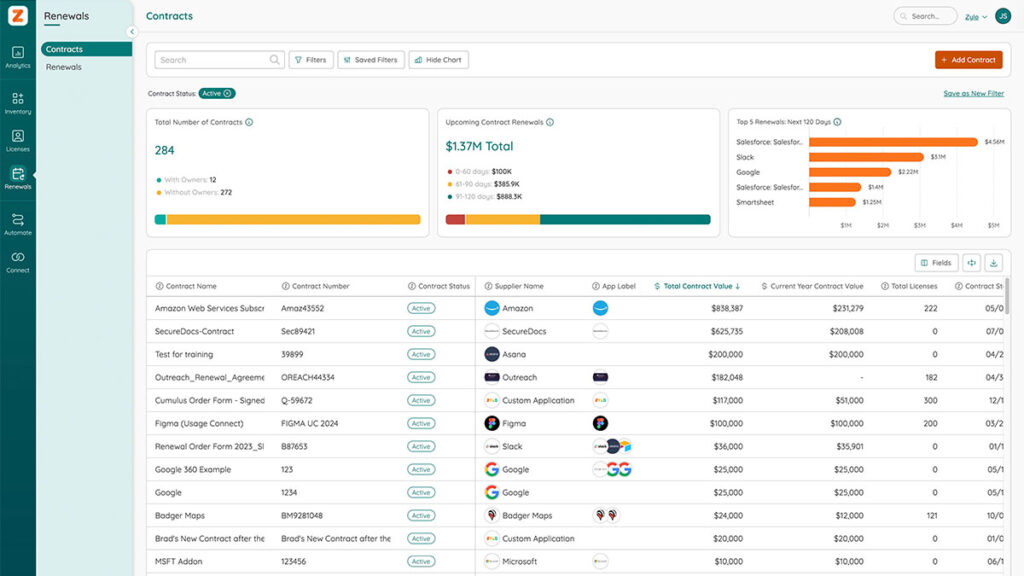
Software Asset Management Tools
In 2025, Software Asset Management tools should include the following capabilities to help SAM professionals reduce spend while maximizing value.
- Software inventory management
- Identify trends with custom dashboards and reports
- Risk management
- Security and compliance
- Software deployment and configuration
- Access and identity management
- Automate IT processes
- License management
- Integrations
- Software application usage tracking and reporting
- License provisioning and deprovisioning
- Renewal management
- Software procurement
- Software contract management
- Vendor management
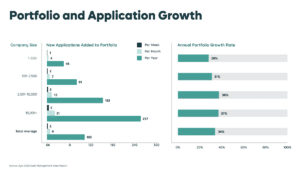
While modern SAM tools oversee the full lifecycle of software assets, the gap between traditional SAM platforms and SaaS Management Platforms (SMPs) has widened significantly. As portfolios grow—an average of 7.6 new apps added per month—organizations need tools that can keep pace. SMPs offer deeper automation, broader coverage, and real-time insights that support today’s decentralized purchasing environment, where shadow IT now represents 33.6% of all apps and spending continues to rise.
Software Inventory Management
Software inventory management gives you a complete view of your application portfolio, along with the security and financial risks associated with each tool. Traditional SAM tools primarily track on-premises software, while SMPs provide complete SaaS visibility—critical at a time when portfolios now average 275 applications and continue to expand.
Real-time discovery helps you avoid blind spots that often lead to waste, especially as more purchases shift to business units and IT manages a smaller share of total spend.
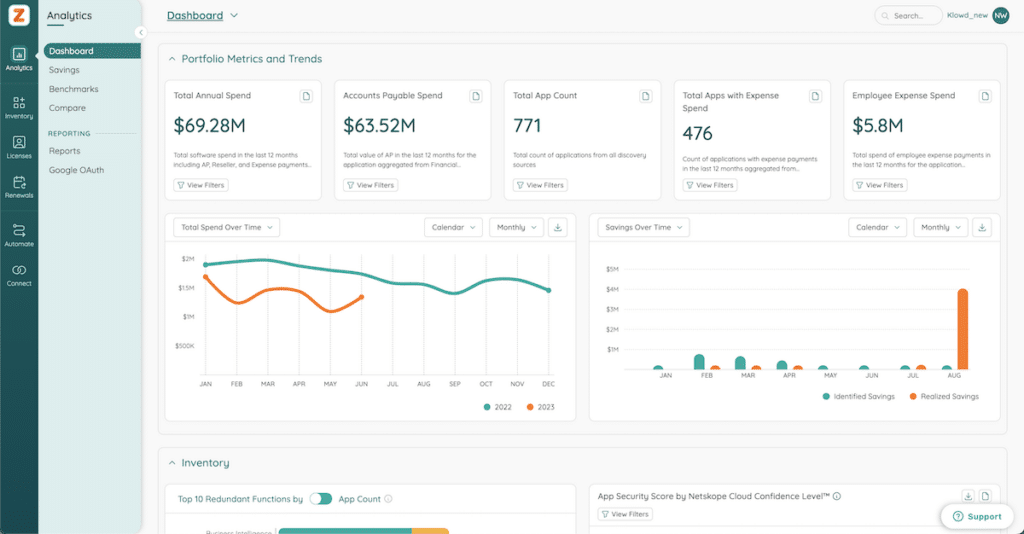
Identify Trends with Custom Dashboards and Reports
Dashboards give you clear, accessible insights into usage, spend, and risk across your SaaS estate. SMPs take this further by aggregating data across all applications, making it easier to uncover redundant tools, multi-channel spend, and low-value licenses.
This matters because a large share of SaaS licenses remains unused each month, resulting in significant waste for most organizations. Tailored dashboards help you pinpoint the highest-impact opportunities, prepare for audits with current data, and share insights consistently across teams.
Risk Management
SAM tools help you surface financial, operational, and security risks that emerge across your portfolio. As decentralized purchasing becomes more common, hidden risks grow—employees regularly introduce new tools into the business without a formal review.
SMPs strengthen your ability to manage these risks with continuous monitoring of spending, usage, and security posture. Many expensed and unmanaged apps still show weak security performance overall, making it even more important to have centralized visibility.
Security and Compliance
Traditional SAM tools rely heavily on manual processes to track compliance, increasing the risk of something slipping through the cracks. SMPs automate these insights across your entire SaaS stack, flagging orphaned licenses, unmanaged accounts, and tools lacking important security certifications such as SOC 2.
Many applications still sit outside your identity governance systems, leaving gaps that can expose your organization to unnecessary risk. Using SMP insights, you can work more effectively with your Security and InfoSec teams to tighten access and improve your compliance posture.
Software Deployment and Configuration
SAM tools help you deploy and configure software in a structured way to maintain compliance and maximize value. SMPs extend this support by helping you manage SaaS deployments at scale and by integrating directly with ITSM workflows, streamlining approvals and provisioning for all applications—not just core systems.
Access and Identity Management
SAM tools help you track provisioning activity, while SMPs give you an even clearer view by integrating with identity platforms like Okta. This lets you spot unused access, risky entitlements, and compliance gaps across your application ecosystem.
While SMPs strengthen your visibility, they’re not a substitute for dedicated access and identity management tools. Instead, they work alongside those systems—giving you the continuous SaaS insights you need while your identity tools handle enforcement, authentication, and deeper acc
Automate IT Processes
Automation is essential as SaaS adoption accelerates. SAM tools automate license tracking for traditional software, while SMPs automate broader workflows such as access reclamation, renewal alerts, usage auditing, and reporting.
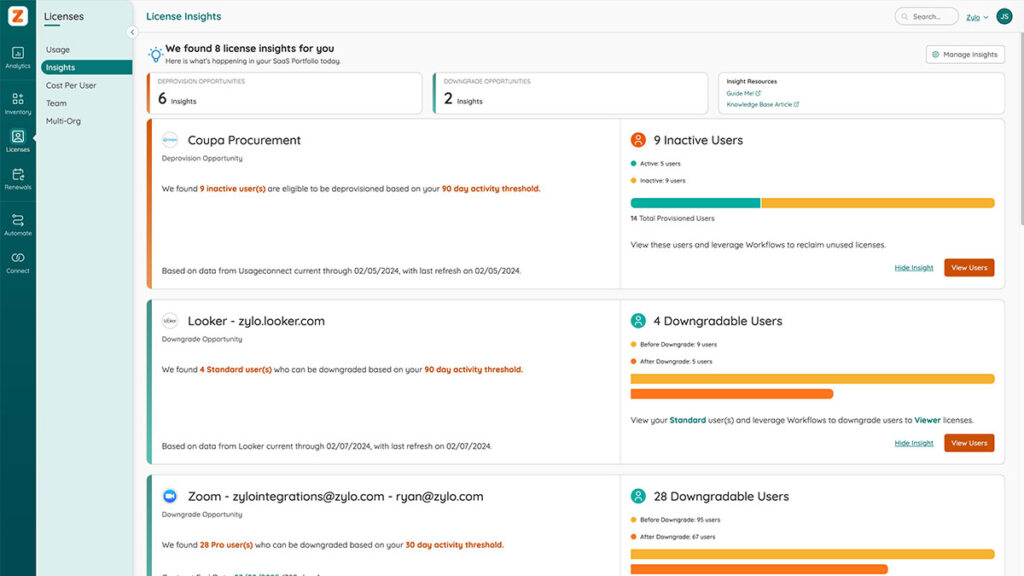
Automation directly correlates with waste reduction. ModMed, for example, ran 82 license deprovision workflows, generating $913,576 in savings and achieving 75.3% utilization
License Management
License management helps you rightsize access and avoid unnecessary spend. With utilization rates often lower than expected, keeping a close eye on usage becomes essential.
Traditional SAM tools lean on manual audits, while SMPs automate key activities like usage insights, reclamation workflows, and renewal analysis. These capabilities help you keep pace with modern licensing models, which many IT leaders still find increasingly complex to manage.
Integrations
Integrations expand your visibility across the systems you rely on every day. Traditional SAM tools focus on large on-prem titles, while SMPs integrate with a wider range of SaaS applications and break down usage to a more detailed level. This enables more precise optimization across sanctioned purchases, shadow IT, and team-level acquisitions.
Software Application Usage Tracking and Reporting
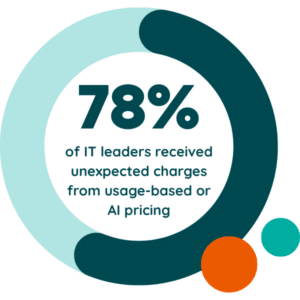
Usage tracking ensures your licenses match real business needs. SAM tools provide basic tracking for core applications, while SMPs offer real-time usage insights across your entire portfolio. This level of detail becomes especially important as you prepare for renewals or face pricing changes linked to consumption and AI-driven features—factors that increasingly catch organizations off guard.
License Provisioning and Deprovisioning
Provisioning ensures employees have the access they need, while deprovisioning helps you eliminate waste and reduce security risk. SMPs help automate these steps, significantly cutting down on dormant accounts and keeping your environment cleaner and more efficient.
Renewal Management
Without complete visibility into usage, spend, and contract terms, renewals can quickly lead to overpayments. Traditional SAM tools track only select agreements, while SMPs centralize contract data, spend histories, and renewal calendars. This gives you a clearer path to negotiate fair terms and avoid unnecessary commitments.
Software Procurement
SAM tools serve as a system of record for core software purchases. SMPs add visibility into every channel where software enters your organization—including purchases made by teams and individual employees. This helps you identify duplicate purchases and uncover spend you may not otherwise see.
Software Contract Management
Contract management keeps you compliant and supports better negotiation outcomes. SAM tools offer basic contract tracking, while SMPs add automated alerts, renewal insights, and complete portfolio visibility. This helps you benchmark terms more effectively and avoid contracts that no longer serve your needs.
Vendor Management
Vendor relationships shape pricing, adoption, and long-term value. Traditional SAM tools focus primarily on large, established vendors. SMPs expand this visibility across all vendors—including unmanaged or shadow IT tools—so you can consolidate, compare value, and negotiate from a stronger position.
How to Choose the Right SAM Software
As you evaluate SAM software, use the following considerations to guide your decision:
- Flexibility to manage software holistically
- Scalability as your business grows
- Integration capabilities
- Automated discovery
- Access controls for security and compliance
- Automated renewal tracking
- Experience and reputation
- Support and training
- Pricing model
Choosing the right Software Asset Management software is one of the most important steps you can take to control costs, improve compliance, and manage both on-premises and SaaS environments effectively. Select a platform that supports your needs now and in the future as your environment grows. We recommend asking these five questions when evaluating a SAM tool.
Flexibility to Manage Software Holistically
Look for a solution that supports the mix of tools you already have. Most enterprises rely on both on-premises software and a growing list of SaaS applications, so one platform rarely covers everything. Traditional SAM tools still play an important role in managing core on-prem titles, while SaaS Management platforms extend your visibility across subscriptions, usage, and shadow IT.
Using a combination of tools is often the most effective approach for gaining complete visibility and balancing oversight across both environments and adapting as your needs evolve.
“You need to have both [a SMP and SAM tool], because you have two fundamentally different types of software in the enterprise.”
— Jason Owens, ITAM Leader at Netflix
Scalability as Your Business Grows
Choose a tool that can scale with your organization. SaaS portfolios expand quickly, and new apps show up far more often than most teams expect. Instead of relying on manual updates or rigid systems, look for a platform designed to handle constant growth and the increasing complexity that comes with AI tools, decentralized purchasing, and ongoing SaaS sprawl.
A scalable system ensures you maintain performance, visibility, and governance even as your application footprint becomes larger and more distributed.
Integration Capabilities
Prioritize tools that connect smoothly with your existing systems. Strong integrations with procurement, HR, finance, and identity providers give you a single, reliable system of record. What matters most is the depth of the integration—not just the number of connectors. Look for usage-level, SKU-level, and entitlement-level insights that help you understand who is using what and where waste may be hiding.
SMPs tend to offer the most complete view, giving you the real-time data you need for accurate optimization and better renewal planning.
Automated Discovery
Make sure the platform you choose can automatically detect new software, especially SaaS tools purchased outside IT. Most traditional SAM platforms only capture what is already centrally managed. SMPs continuously scan for new applications—department-managed, employee-purchased, or expensed—so you know what’s entering the environment before it becomes a risk or an unnecessary cost.
If the tool includes financial discovery, you’ll gain even earlier visibility into shadow IT and unplanned spend.
Access Controls for Security and Compliance
Look for role-based access controls, detailed entitlement mapping, and integrations with identity providers such as Okta. These features make it easier for you to see who has access, address gaps, and understand where policy updates may be needed. SMPs often excel in surfacing unmanaged accounts and hand-offs tied to former employees, helping you strengthen your overall identity governance.
Automated Renewal Tracking
Choose a solution that helps you stay ahead of renewals. Many on-prem SAM tools provide only limited renewal oversight, which can lead to rushed decisions or overpayments. SMPs centralize contract terms, spend history, and key dates, and provide automated reminders and workflows so you can approach renewals with confidence and from a position of strength.
Experience and Reputation
Select a vendor with a proven record of supporting environments like yours. Analyst research, peer reviews, and customer feedback—all available through sources such as Gartner Peer Insights—can help you understand a vendor’s reliability, roadmap maturity, and long-term support quality. A strong partner will guide you through implementation and continue to support your evolving needs.
Support and Training
Good support can make or break your program. Look for a vendor that provides clear onboarding, responsive customer service, and accessible training resources. You want a partner that helps your team build confidence quickly and resolves issues without slowing down your operations.
Pricing Model
Evaluate how each vendor’s pricing structure aligns with your environment. Traditional SAM platforms often involve larger upfront investments and longer implementations, while SaaS Management platforms generally deliver faster time-to-value and more flexible pricing.
If you’re starting a software management program, beginning with an SMP often gives you the quickest return—value is typically realized in weeks or months instead of quarters.
2024 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for SaaS Management Platforms
Learn MoreThe Disadvantages of Spreadsheets & Why SAM Software Is Better
Using spreadsheets to manage software assets may seem straightforward, but it creates inefficiencies, hidden costs, and compliance risks. SAM software centralizes and automates software management, improving accuracy, oversight, and decision-making. These are the key reasons SAM tools outperform spreadsheets:
- Licenses are easy to overlook
- AI is changing expectations for software management
- Data quality is questionable
- Cloud-based software is not centralized
- SAM involves multiple stakeholders
- License metrics are complex
- Monitoring and tracking software usage
Licenses Are Easy to Overlook
Spreadsheets are error-prone and often contain outdated information, making it easy to miss renewals or overlook unused licenses. SAM software automates tracking, flags underused subscriptions, and alerts teams to upcoming renewals—reducing the risk of surprise fees and overages.
AI Is Changing Expectations for Software Management
The rapid growth of AI-driven tools makes manual tracking even less practical. Employees adopt new applications faster than spreadsheets can be updated, and many AI tools use consumption-based pricing models that shift month to month. SAM software provides real-time discovery, usage monitoring, and automated alerts that help teams stay ahead of both cost spikes and risk. This level of automation is essential as portfolios expand and purchasing continues to decentralize.
Data Quality Is Questionable
Spreadsheets require manual updates, increasing the risk of inaccurate or incomplete records. SAM software delivers real-time accuracy by automatically updating license data, usage, compliance status, and inventory. This ensures decisions are based on current and complete information.
Cloud-Based Software Is Not Centralized
With spreadsheets, it’s difficult to track cloud and SaaS tools because they rely on manual entry—and only capture applications IT already knows about. SAM platforms centralize data across on-premises, SaaS, and shadow IT, giving teams a clearer view of their full software footprint.
SAM Involves Multiple Stakeholders
Software management spans IT, Procurement, Finance, and Security. Spreadsheets often live in silos, with separate versions maintained by different teams. SAM software solves this by centralizing data and enabling shared visibility, helping stakeholders collaborate more effectively.
License Metrics Are Complex
License types vary widely—seat-based, usage-based, role-based, storage-based, and more. Manually calculating entitlements and compliance introduces frequent errors. SAM software automates these calculations, ensuring accurate usage measurement and reducing the risk of misalignment with contract terms.
Monitoring & Tracking Software Usage
Spreadsheets cannot monitor usage or adoption trends. SAM software continuously tracks real-time usage across applications, making it easier to identify waste, support renewals with accurate data, and reallocate licenses based on actual demand. This visibility helps teams make faster, more informed decisions about upgrades, consolidations, and retirements.
How to Get Started with a Software Asset Management Program
Launching a Software Asset Management program may feel overwhelming, but a structured approach helps teams gain visibility, reduce waste, and stay compliant. To begin your SAM program, follow these steps:
- Assess your software environment
- Document and standardize your procurement processes
- Audit software licenses and subscriptions
- Clean up and organization your license inventory
- Determine software usage
- Implement your program
- Track software assets over time
- Monitor and optimize software usage
Step 1: Assess Your Software Environment
Begin with a full assessment of your software environment. Identify all on-premises and SaaS applications, review usage, and confirm licensing and compliance status. Use these insights to surface duplicate tools, underutilized apps, and potential risks. Continuous discovery is essential for maintaining visibility and sustaining long-term cost savings.
Step 2: Document and Standardize Your Procurement Processes
A consistent procurement process reduces shadow IT and improves financial control. Standardize how software is requested, purchased, and approved to ensure that licensing, renewals, and security requirements are met before tools are adopted.
Step 3: Audit Software Licenses and Subscriptions
Audit your licenses and subscriptions to verify compliance with vendor terms. This step helps uncover unused licenses that can be reclaimed, identify entitlement gaps, and highlight opportunities to consolidate overlapping applications.
Step 4: Clean Up and Organize Your License Inventory
Centralize all license information in one system of record. SAM platforms automatically update inventories, making it easier to track entitlements, eliminate duplicates, and maintain accuracy without manual effort.
Step 5: Determine Software Usage
Understanding real usage is key to optimization. Use SAM or SaaS Management tools to monitor adoption, identify underutilized applications, and determine where licenses can be reallocated or removed ahead of renewals.
Step 6: Implementation
Configure your SAM tool, connect it to systems such as procurement, HR, identity providers, and finance, and train the teams who will use it. Strong implementation ensures early wins and smoother long-term adoption.
Step 7: Track Software Assets
Track assets continuously to maintain compliance and control costs. Ongoing monitoring helps teams stay ahead of renewal deadlines, identify new applications entering the environment, and catch emerging risks before they escalate.
Step 8: Monitor and Optimize Software Usage
After your SAM program is in motion, focus on ongoing optimization. Real-time reporting highlights where licenses can be reclaimed, which apps no longer deliver value, and what tools can be consolidated. Regular optimization ensures software stays aligned with business needs as portfolios evolve.
Software Asset Management Best Practices
Following best practices helps organizations maintain control, strengthen compliance, and get more value from their software investments. These core practices support a strong, sustainable SAM program:
- Regular software audits
- Training and awareness
- Continuous discovery
- Strengthen renewal planning and preparation
- Use real-time usage insights to drive optimization
Regular Audits
Regular audits ensure compliance with licensing agreements and help surface opportunities for optimization. For on-premises software, audits validate license entitlement and positioning. For SaaS, audits focus on usage, governance, and identifying unused or duplicate subscriptions. SAM and SaaS management tools streamline this work by maintaining accurate inventories and providing real-time visibility across applications.
“Any security person will tell you: you can’t secure what you don’t know you don’t have.”
— Jennifer Clark, IT Asset Manager at Hyatt Corporation
Training and Awareness
Educating employees on software policies and request procedures reduces the risk of shadow IT and helps maintain compliance. Ongoing training ensures staff understand how to properly access and use tools in line with organizational guidelines. Clear communication and executive visibility also support better decision-making around renewals, adoption, and long-term planning.
Implement Continuous Discovery
Continuous discovery helps teams stay aware of new applications entering the environment. It maintains an accurate system of record by identifying tools early, highlighting risks, and ensuring nothing slips outside established policies. This ongoing visibility allows SAM teams to act proactively rather than reacting to surprises.
Strengthen Renewal Planning and Preparation
Strong renewal planning starts with clear visibility into contract terms, usage, and ownership. Reviewing these details early helps determine whether to renew, reduce, consolidate, or retire applications. This preparation supports more informed negotiations and prevents last-minute decisions driven by vendor deadlines.
Use Real-Time Usage Insights to Drive Optimization
Real-time usage insights show whether applications are adopted, underutilized, or misaligned with business needs. These signals guide license reallocations, identify tools that may need additional support, and inform renewal decisions. Consistent optimization keeps the portfolio efficient and aligned with organizational goals.
Stages of Software Asset Lifecycle Management
Understanding the stages of the software asset lifecycle helps you manage every application with clarity and consistency. These stages include:
- Establishing needs, planning, and budgeting
- Evaluating and procuring the right software
- Deploying applications and managing inventory
- Ensure ongoing compliance and governance
- Optimizing usage and aligning licenses to demand
- Managing maintenance and application health
- Tracking performance and reporting insights
- Retiring or disposing of software responsibly
When each phase is defined, you can track what you own, how it’s used, and when it needs attention. This structure makes it easier for you to control spending, stay compliant, and make confident decisions as your portfolio grows.
Establishing Needs, Planning, and Budgeting
Lifecycle management begins with understanding your business needs and how new software fits into your larger priorities. This stage often includes:
- Assessing requirements
- Evaluating gaps in existing tools
- Determining whether new technology is necessary
Precise budgeting ensures you allocate the right resources from the start and avoid overspending on tools that don’t align with strategic goals. Strong planning also sets expectations around ownership, implementation timelines, and long-term governance.
Evaluating and Procuring the Right Software
During procurement, you focus on selecting tools that meet business, technical, and security requirements. This involves:
- Reviewing vendor offerings
- Assessing feature and capability fit
- Confirming licensing models
Collaboration between IT, Procurement, Finance, and Security ensures new applications meet your standards before purchase. Effective procurement helps you prevent redundant tools from entering the environment and ensures contracts reflect real needs and usage expectations.
Deploying Applications and Managing Inventory
Once you choose the right software, it needs to be deployed consistently and documented accurately. Deployment typically includes:
- Configuring access
- Integrating the tool with existing systems
- Ensuring required controls are in place
Inventory management tracks where software is installed, who has access, and how each tool fits into your broader portfolio. A reliable inventory prevents duplicate purchases, supports compliance, and gives you a foundation for ongoing optimization.
Ensuring Ongoing Compliance and Governance
Compliance requires monitoring whether software is used according to vendor agreements and your internal policies. Governance frameworks define:
- How tools are requested
- How they’re approved
- How they’re assigned
This stage also involves maintaining accurate records of licenses, usage limits, and entitlement data. Continuous oversight reduces risk, supports audit readiness, and ensures your software remains aligned with regulatory and contractual obligations.
Optimizing Usage and Aligning Licenses to Demand
Usage optimization helps you ensure each application delivers value and that licenses match real demand. You may:
- Review adoption and feature use
- Evaluate user-level activity
- Identify consolidation or reallocation opportunities
Optimization can involve removing unused licenses, shifting users to more appropriate tiers, or consolidating similar tools to keep your portfolio efficient and prevent unnecessary spend.
Managing Maintenance and Application Health
Maintenance keeps your applications stable, secure, and up to date. This includes:
- Applying patches
- Updating versions
- Reviewing vendor release notes
You also monitor how changes affect integrations, performance, and user experience. Routine care prevents disruptions, reduces support issues, and extends the useful life of your applications.
Tracking Performance and Reporting Insights
Reporting gives you visibility into how software supports your business objectives. Teams track key metrics such as:
- Adoption trends
- Renewal timelines
- Compliance risks
Clear reporting keeps stakeholders informed, supports budgeting discussions, and highlights applications that may need additional enablement or review.
Retiring or Disposing of Software Responsibly
When software no longer meets your needs, it must be retired in a controlled and secure way. Retirement usually involves:
- Removing access
- Decommissioning licenses
- Ensuring data is handled according to policy
Proper disposal also involves updating inventories, notifying stakeholders, and determining whether the tool should be replaced or fully eliminated. A structured retirement process prevents security gaps and reduces ongoing costs.
Overcoming the Risks and Challenges of SAM Implementation
Implementing a Software Asset Management program brings several challenges, especially as software portfolios continue to grow and purchasing becomes more decentralized. The most common risks include:
- Shadow IT
- SaaS Sprawl
- Tracking licenses and renewals
- Ensuring continuous compliance
- Unused or abandoned software licenses
- Duplicate subscriptions
- Noncompliance with licensing agreements
- The growing impact of AI
Shadow IT
Business units and employees are now responsible for the majority of spend and application adoption—outside of IT oversight. This creates blind spots that lead to:
- Unmanaged risk
- Redundant tools
- Inconsistent security controls
SaaS Management platforms surface these hidden applications through automated financial discovery, giving teams the visibility needed to evaluate tools, enforce policies, and eliminate unmanaged risk.
SaaS Sprawl and Tracking Licenses and Renewals
Large organizations often operate massive application portfolios, and new tools are added constantly through decentralized purchasing.
This creates challenges such as:
- New applications entering the environment without oversight
- Legacy tools capturing only known or IT-managed software
- Unsanctioned purchases remaining untracked
- Renewals spread across teams, budgets, and systems
SaaS Management platforms address these issues by:
- Automating discovery so new purchases surface immediately
- Centralizing renewal data to reduce manual tracking
- Helping you manage contracts proactively
- Preventing surprise costs tied to overlooked or unplanned renewals
- Reducing the operational burden of tracking hundreds of subscriptions
Ensuring Continuous Compliance
A significant share of expensed and department-managed applications fail to meet internal security or compliance standards. When tools fall outside required certifications or policy frameworks, organizations face both operational and regulatory risk. SAM software continuously monitors for noncompliant applications, flags governance gaps, and helps teams enforce standards before issues escalate.
“In today’s workplace, the breadth of tooling and flexibility is great for productivity. But it means IT, Cybersecurity, and Finance teams must enable it without putting the enterprise under more stress or risk of a malicious or inadvertent breach or loss of data, let alone inefficient spending.”
— David Willis, VP of Technology Integrations at Netskope
Unused or Abandoned Software Licenses (Zombie Accounts)
Zombie applications and unused licenses contribute heavily to software waste. Across large organizations, a significant portion of licenses remain unutilized, often tied to former employees or outdated use cases. SAM platforms surface inactive accounts, highlight where reassignment or reclamation is needed, and automate workflows to recover licenses. This helps reduce waste and ensures investments align with actual business needs.
Duplicate Subscriptions
Duplicate subscriptions occur when different teams or individuals purchase similar tools independently. These redundancies drive up costs and create fragmented data and workflows. SAM platforms flag overlapping applications, helping organizations consolidate vendors, negotiate stronger terms, and support more unified collaboration.
Noncompliance with Licensing Agreements
Licensing rules vary widely by product and vendor, making compliance difficult to maintain through manual processes. Real-time visibility into license positioning, usage, and entitlements helps teams stay ahead of overages and avoid penalties. SAM platforms simplify compliance by tracking license assignments and ensuring they align with contract terms throughout the lifecycle.
The Growing Impact of AI on SAM Risk
AI-driven tools and copilots are entering your organization quickly, often through departmental budgets or employee-led experiments. Many rely on consumption-based pricing or tiered add-ons, which makes costs harder to predict and track manually. These tools can also introduce data-handling and security considerations that legacy SAM processes may overlook.
SAM platforms help you manage this new category by:
- Identifying emerging AI applications early
• Tracking entitlements and usage trends
• Ensuring appropriate controls are in place before adoption scales
The Future of SAM Is SaaS: Looking Beyond 2026
Software Asset Management is evolving quickly as organizations move into a SaaS-first world. With decentralized purchasing, rapid AI adoption, and constant turnover in applications, manual processes can’t keep up. Modern SAM now relies on continuous discovery, real-time usage insights, and automated visibility.
A SaaS-focused approach gives you the control to reduce waste, operate efficiently, and keep software aligned with business goals. Zylo’s platform supports this shift by centralizing application data, automating renewals, and strengthening procurement alignment. With the right tools and processes, SAM becomes a strategic driver of cost savings, compliance, and operational clarity.
Explore Zylo for software asset management. Connect with our team of experts today for a personalized demo.
FAQs about Software Asset Management
What does software asset management do?
Software Asset Management tracks and governs software across the organization. It ensures licenses are used correctly, reduces unnecessary spend, and improves compliance. SAM also provides clear visibility into which software is owned, who uses it, and how it supports business needs.
What does a SAM tool do?
A SAM tool centralizes license, usage, and contract data. It automates tasks such as usage tracking, entitlement management, and audit preparation. SaaS management platforms extend this with real-time discovery, identity integrations, and deeper insights for renewals and procurement.
Is software asset management part of ITIL?
Yes. SAM is part of IT Asset Management within ITIL. It supports service management by ensuring software is tracked, controlled, and used efficiently throughout its lifecycle.
What is the ROI of SAM?
SAM delivers ROI by reducing waste, rightsizing software, and improving negotiation leverage. Savings often come from unused license reclamation, avoiding audit penalties, and preventing duplicate purchases.
Why is software asset management important for businesses?
SAM helps organizations control costs, limit compliance risk, and strengthen security. It also provides the visibility needed to manage growing portfolios and decentralized purchasing.
How can software asset management help reduce costs?
SAM reduces costs by identifying unused licenses, consolidating redundant tools, and right-sizing renewals. It also helps avoid noncompliance penalties that can unexpectedly increase spend.
What are the key components of a software asset management program?
Key components include:
- Software inventory management
- License tracking and usage monitoring
- Contract and vendor management
- Renewal planning and compliance oversight
What tools and technologies are commonly used in software asset management?
Organizations typically use:
- SAM and SaaS management platforms
- Identity and access management tools
- Procurement and contract management systems
- ITSM platforms for workflow automation
What is the software asset management lifecycle?
The SAM lifecycle covers the full journey of a software asset—from evaluation to procurement, deployment, optimization, renewal, and retirement. It ensures software remains cost-effective, compliant, and aligned with business needs.
What are the key stages of asset life cycle management?
Common stages include:
- Assessment
- Procurement
- Deployment
- Usage monitoring
- Optimization
- Renewal
- Retirement




 — Jason Owens, ITAM Leader at Netflix
— Jason Owens, ITAM Leader at Netflix


 —
—  — David Willis, VP of Technology Integrations at Netskope
— David Willis, VP of Technology Integrations at Netskope