
Why Ongoing Discovery of Longtail SaaS Apps Is Critical
Table of Contents ToggleWhat Are Longtail SaaS Applications?The Rise of Longtail...
Back
Back
Search for Keywords...
Blog

Table of Contents
Each tool in your software stack should deliver business value. That’s where technology rationalization comes in. Instead of juggling hundreds of tools with overlapping features, you can pinpoint redundancies, remove waste, and make decisions that strengthen your organization’s long-term strategy.
With SaaS portfolios continuing to grow at a rapid pace, taking control of your technology stack ensures efficiency today and flexibility for tomorrow. In fact, Gartner’s March 2025 Cost Optimization Pulse found that nearly 70% of CIOs list technology rationalization as a top initiative for reducing IT waste. Are you ready to follow suit?
Technology app rationalization is the process of reviewing and evaluating your organization’s software portfolio to determine which tools provide value and which should be consolidated, replaced, or retired. With the average organization averaging 275 apps in their portfolio in 2025, rationalization is more important than ever.
Because different teams and vendors often use different terms for the same process, it’s important to recognize these variations and classify them consistently. The following terms are commonly used when discussing technology rationalization.
This term describes the structured evaluation of applications across the business. It focuses on identifying which tools to keep, replace, consolidate, or retire based on business need and cost efficiency.
This phrase expands the scope beyond applications, covering infrastructure, hardware, and systems. It ensures the entire IT environment aligns with strategy and eliminates waste.
Optimization focuses on enhancing the value of the applications you retain. It balances cost-cutting with maximizing ROI and adoption.
Consolidation reduces the number of platforms and systems in use. Fewer overlapping systems means improved integration, streamlined support, and reduced licensing costs.
Standardization ensures teams operate from a consistent set of platforms. This reduces training, improves collaboration, and supports compliance.
This approach evaluates all IT resources, not just applications, to maximize return on investment. Often tied to ITAM, it ensures assets are used efficiently and strategically.
Application rationalization delivers measurable business value by cutting costs, reducing risk, and improving efficiency. Organizations that take a structured approach see benefits across:
The following outcomes represent the most important advantages.
Rationalization helps you remove redundant or outdated tools that drain budgets without delivering value. By consolidating functionality and retiring underused applications, organizations lower overall SaaS spend and free up resources for higher-impact investments.
The risk? Gartner data shows that through 2027, organizations that fail to attain centralized visibility and coordinate SaaS life cycles will overspend on SaaS by at least 25% due to unused entitlements and unnecessary, overlapping tools.
Unsupported applications pose security and compatibility risks. Replacing them ensures your technology stack stays current, stable, and compliant with vendor and regulatory requirements.
Think of Google’s long list of discontinued services—applications once considered essential, only to be phased out over time. Software products can disappear unexpectedly due to acquisitions, declining usage, or vendor shutdowns, leaving organizations scrambling to find replacements.
With a structured application rationalization framework, businesses can:
This proactive approach helps minimize risk, ensure business continuity, and avoid costly last-minute migrations.
Retiring unmanaged or non-compliant apps reduces vulnerabilities. A rationalized environment makes it easier to:
Streamlined technology reduces tool confusion and improves adoption. Employees spend less time switching between systems and more time using applications that truly help them succeed.
Rationalization brings visibility into unsanctioned apps purchased outside of IT oversight. In 2025, it accounts for 3.8% of an organization’s SaaS spend and 33.6% of total applications. Eliminating shadow IT improves security while centralizing spend and usage data.
A consistent set of approved tools:
Without clear guidelines, different teams often select their own tools, leading to SaaS sprawl and a fragmented software environment. This lack of standardization results in compatibility issues, data silos, and inconsistent workflows that slow down operations.
Application rationalization helps establish a unified approach to software selection and usage. By identifying the most effective tools and eliminating unnecessary overlap, companies can ensure all teams work within a standardized software ecosystem.
Adobe Drives Innovation and Massive Savings with Zylo
In the past 4 years, Adobe has rapidly scaled from $9B to $18B. This growth has made an already complex environment even more complex. Learn how they leveraged Zylo to get complete visibility into their SaaS portfolio, unlock millions in cost savings and avoidance and improve the employee experience.
A clear view of application usage and spend allows leaders to make data-driven decisions. These insights help guide renewals, consolidate contracts, and prioritize investments that align with strategic goals.
Reducing the number of overlapping platforms makes it easier for IT to:
A rationalized environment ensures data flows more easily across systems. Better integration reduces silos and supports analytics, reporting, and automation initiatives.
Fewer redundant apps mean fewer entry points for attackers. Rationalization strengthens the security posture by ensuring all applications are monitored, compliant, and properly maintained. Gartner analysts found that 41% of employees acquire, modify, or create technology that their IT departments are unaware of, a number expected to rise to 75% by 2027.
Rationalization connects IT spend directly to business outcomes. Each retained application supports a defined purpose, helping organizations meet goals while controlling costs.
Fewer, better-managed contracts give procurement teams more leverage. Consolidating vendors creates opportunities to secure discounts, favorable terms, and improved support.
A leaner, well-managed stack allows organizations to adapt quickly. When market conditions change, it’s easier to shift resources and deploy new tools strategically.
Organizations pursue application rationalization in response to cost pressures, business changes, and operational risks. The following factors commonly drive organizations to evaluate their software portfolios:
Shifting workloads to the cloud often reveals redundant or outdated applications. Rationalization ensures only valuable tools make the transition, lowering your migration costs and reducing complexity.
When companies merge, duplicate systems and overlapping licenses create waste. Rationalization helps you unify your technology stacks, standardize platforms, and cut unnecessary spend.
“Having an instance of Zylo for Marigold and the acquired company allows us to connect to their finance systems and pull in that data. And then we’re doing an instant-compare of what tools are the exact same.”
— Karen Hodson, Global Procurement & Real Estate Officer, Marigold
Consolidating operations or business units increases pressure to reduce IT overhead. Rationalization helps identify areas where you can quickly capture cost savings and efficiencies.
New digital initiatives often require fresh applications. Rationalization clears room in the portfolio, ensuring your new investments support engagement without bloating the stack.
Unexpected events—such as economic downturns or security breaches—accelerate the need for efficiency. Rationalization enables you to make quick decisions about which tools to keep and which to cut.
Applications that fail to deliver measurable outcomes are another source of waste. Rationalization provides a framework for evaluating performance and replacing underutilized tools.
Leadership often sets aggressive cost-cutting targets. Rationalization gives IT and procurement a structured process to identify savings without disrupting your operations.
Legacy systems and outdated tools build technical debt over time. Rationalization helps you clear that debt by retiring obsolete technology and modernizing the portfolio.
Uncontrolled app growth leads to shadow IT and ballooning costs. Rationalization brings visibility and governance, ensuring new purchases fit into the overall strategy.
Operating across multiple regions introduces new compliance standards. Rationalization ensures your application portfolio is aligned with local regulations and avoids compliance risks.
Marigold Uses Zylo to Save on Sprawling SaaS Costs & Streamline M&A Technology Integration
Discover how Marigold unlocked the door to nearly $1M in SaaS cost savings with Zylo, while undergoing a M&A tech integration and cutting software waste from their portfolio.
A successful application rationalization strategy creates visibility, strengthens compliance, and ensures technology decisions support long-term business goals. The following objectives represent the core outcomes organizations should target:
Rationalization exposes unused licenses, overlapping tools, and legacy systems that inflate costs. For example, Zylo’s 2025 SaaS Management Index found that 53% of SaaS licenses go unused, costing organizations about $21M annually. Optimizing spend ensures every dollar invested in technology delivers measurable value.
With fewer redundant apps, compliance becomes easier to manage. Rationalization simplifies your:
“We wanted to really focus on bringing everything together in one source to make our audit requests a lot easier.”
— Jennifer Clark, Global IT Asset Manager at Hyatt Corporation
Clear visibility into the portfolio helps leaders prioritize the right investments. Rationalization provides the data needed to support renewals, consolidations, or new purchases with confidence.
A rationalized portfolio offers transparency across departments and business units. This visibility reduces duplication, improves collaboration, and ensures IT can proactively manage the environment.
Rationalization supports stronger governance frameworks by centralizing oversight of software decisions. Clear ownership reduces shadow IT and strengthens accountability across stakeholders.
By removing low-value tools and standardizing on approved platforms, your employees face less confusion and achieve higher adoption rates. This leads to better productivity and more consistent results for your company.
Rationalization ensures today’s portfolio aligns with tomorrow’s strategy. Retaining the right tools creates a foundation for modernization, innovation, and future digital initiatives.
Executing an application rationalization strategy can be complex, as organizations often face cultural, technical, and financial obstacles. At Zylo, we frequently see these challenges:
Application rationalization requires buy-in across IT, finance, procurement, and business leaders. Without strong sponsorship, efforts stall due to competing priorities.
Zylo data shows that, on average, IT owns just 26% of total spend and 16% of applications. With the majority of software purchases made outside of IT, it limits visibility into the full portfolio. These organizational silos make it difficult to consolidate or standardize software..
Rationalization takes time and expertise. Limited resources can slow progress, particularly if there is no dedicated team or funding to manage the initiative.
Consolidation can create disruption if multiple business units rely on similar tools. Managing these transitions requires careful planning and clear communication.
Retiring or replacing applications become more challenging due to:
Technical debt must be accounted for in any plan.
Incomplete or inaccurate data about usage, contracts, or costs leads to poor decisions. A reliable inventory and monitoring system is critical for success.
Employees may resist losing familiar tools, even if replacements are more effective. Change management and training are essential to ease adoption.
Organizations that have tried and failed at rationalization in the past may encounter skepticism. Addressing lessons learned helps build credibility and momentum.
Unexpected problems—such as vendor pushback, hidden dependencies, or regulatory changes—often arise. Preparing contingency plans ensures rationalization stays on track.
Securing buy-in is critical for the success of any application rationalization initiative. Leaders, employees, and stakeholders must see clear value, trust the process, and feel supported throughout.
The following strategies help build confidence and ensure smoother execution:
Connect rationalization directly to strategic objectives—such as growth, efficiency, or compliance. This shows stakeholders that the initiative supports the broader mission.
Leaders respond to numbers. Highlight savings from eliminating redundancy or reducing unused licenses to provide a compelling case for investment and action.
Employees are more likely to adopt changes when they see how rationalization improves their workflows. For example, productivity will increase when employees:
Stakeholders may worry about downtime or losing critical features. To build trust and minimize anxiety:
Ensure your data on usage, contracts, and costs are accurate. This provides credibility and ensures that decisions are fact-based rather than driven by opinion.
Establish policies and ownership around software decisions to ensure rationalization is an ongoing practice. Governance provides accountability and sustainability.
Invite stakeholders into the process from the start to ensure alignment. Early involvement reduces resistance and builds advocates across departments.
For instance, start by gathering data on user sentiment to understand whether employees like the tools they’re using. In addition, connect one on one with users to gain context on how an app is used. This becomes valuable data when evaluating which tools to keep or deprecate.
Share early wins—such as immediate cost savings or improved compliance—to prove the value of rationalization. Celebrating progress maintains momentum and encourages broader support.
The Definitive Guide to SaaS Management
Learn MoreA repeatable process ensures application rationalization delivers consistent results. IT Asset Management (ITAM) is foundational to this approach because it provides the inventory, usage, and cost data required for accurate decision-making.
The following steps outline a proven methodology.
Start with clear goals that guide the rationalization effort. Common business objectives include:
When the scope is clearly defined, it ensures alignment across stakeholders. It should include:
Conduct a discovery exercise to identify all applications in use, including shadow IT. Add this inventory to a SaaS system of record along with
With full visibility, you have a baseline for analysis and identifying redundancies.
Evaluate each application using defined business and technical criteria such as:
Look deeper into the total cost of ownership (TCO) to understand the true financial impact of each tool. TCO includes licensing, hosting, support, integrations, and training.
TCO Formula:
TCO = (License Costs + Hosting Fees + Integration Costs + Support Costs + Training Costs) – (Vendor Discounts or Incentives)
For example, a CRM tool may cost $200,000 in licenses annually, plus $50,000 in hosting, $25,000 in integrations, $30,000 in support, and $20,000 in training. With a $25,000 vendor discount, the TCO equals
TCO = ($200,000 + $50,000 + $25,000 + $30,000 + $20,000) – $25,000 = $325,000
This calculation shows the importance of accounting for every hidden expense when evaluating applications. Licensing alone rarely reflects the actual cost.
After analyzing the software portfolio, sort the applications into action categories to guide the rationalization process.
Keep and continue to monitor applications that:
Software that is outdated, underutilized, or no longer aligns with business objectives should be phased out. When retiring applications, consider:
Some tools may need to be moved to a different hosting environment. For example: an app transitioning from on-premises to the cloud for better performance and scalability.
Replace or upgrade applications if they lack essential features or have become inefficient. This gives way to more modern, cost-effective alternatives.
Establish a roadmap that defines the timeline and sequence for changes. Consider a phased execution, which can reduce disruption and align transitions with business cycles.
Key considerations include:
Implement rationalization decisions that minimize business disruption. This step requires collaboration between IT, finance, security, and business units to ensure a seamless transition.
Key actions during execution:
Using a SaaS Management Platform streamlines execution by providing real-time insights into software usage, license management, and spending, ensuring the process remains data-driven.
Conduct ongoing reviews to ensure the portfolio stays optimized as new applications enter the environment and business needs evolve. An app review should include:
If you want your rationalization strategy to deliver lasting results, you need to treat it as an ongoing practice, not a one-time project. By building good habits into your processes, you’ll keep costs low, strengthen governance, and improve efficiency.
Here are some best practices to follow:
Treat application rationalization as an ongoing function, not just a one-time cleanup. Regular audits and governance policies prevent software sprawl and ensure new applications align with business goals.
You’ll get the best results when IT, finance, procurement, and business units work together. Shared visibility and collaboration prevent redundant purchases and improve decision-making.
Give your teams the tools to succeed by documenting clear processes and offering training. Standard operating procedures make rationalization repeatable and sustainable, even when staff changes occur.
Your employees know which tools actually help them. When you involve them in the process, it:
Keep rationalization from slipping off the radar by scheduling regular reviews. Tracking usage, adoption, and savings helps you determine whether your strategy is working and identify areas for improvement.
What does technology rationalization look like in real life? The following examples illustrate how companies have improved efficiency, reduced costs, and fostered growth through a structured approach.
Adobe reduced SaaS sprawl by consolidating overlapping licenses and retiring outdated tools. This gave employees access to the right applications while freeing up budget for innovation.
Key Business Outcomes:
When Marigold acquired a business, duplicate applications and conflicting systems created inefficiencies. Through rationalization, they built a unified technology stack that simplified operations and saved money.
Key Business Outcomes:
For more real-world examples, explore Zylo’s case studies on how companies successfully optimized their SaaS portfolios.
You can’t manage what you can’t see. The right tools help you uncover what’s in your portfolio, track usage, and monitor compliance. With these capabilities in place, you’ll make rationalization easier and more effective.
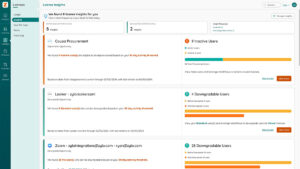
Full visibility into your organization’s SaaS portfolio requires a rationalization tool with robust discovery, like Zylo’s AI-powered model. Automatic categorization provides a strong base to begin your application review.
License tracking is critical to understanding how well a tool is used and adopted. Use a tool like Zylo that tracks real-time user activity and user overlap among redundant software.
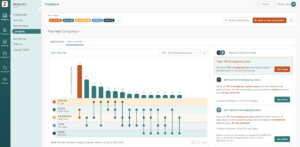
Without a structured approach to SaaS renewals, businesses often overpay for software or miss opportunities to consolidate contracts. Zylo centralizes contract details, automates renewal tracking, and provides data-driven insights for better negotiation.
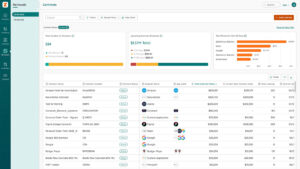
Detailed spend insights point to waste and redundancy. With this visibility, you’ll find opportunities to consolidate contracts, reduce costs, and optimize your budget.
For example, Zylo helps organizations:
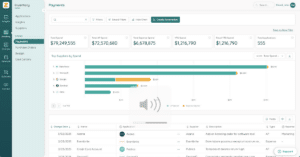
Factoring an application’s risk level is an essential part of your rationalization decision, so the platform you use should provide those insights. With Zylo, IT teams can quickly identify which applications store sensitive customer information, such as PII or financial data, and take action to secure that data.

AI is transforming how you can approach rationalization through:
By automating manual work and providing predictive insights, AI enables you to act faster, reduce waste, and maximize the value of your technology investments.
AI can highlight usage trends and flag applications that may soon be redundant. This gives you the chance to act proactively rather than reactively.
With AI automating discovery, license tracking, and reporting, you’ll spend less time on manual tasks and more time focusing on strategic improvements.
AI gives you data-backed recommendations, so you can compare scenarios and make confident decisions about what to keep, consolidate, or replace.
Multi-cloud environments are complex. AI helps you identify underutilized resources and redundant services, making it easier to streamline and control cloud spend.
Application rationalization helps simplify your stack, reduce risk, and realize cost savings. With Zylo, you gain the insights and governance to keep your SaaS portfolio efficient, secure, and ready to support your growth. Ready to see how Zylo can help you take control of your SaaS portfolio?
Request a demo today and start making smarter application decisions.
Application rationalization evaluates an organization’s software portfolio to determine which applications should be retained, replaced, consolidated, or retired based on business value, cost, and usage.
Application rationalization helps reduce software costs, improve operational efficiency, enhance security, standardize tools, and align IT investments with business objectives.
Common challenges include lack of visibility, resistance to change, and resource constraints. These can be addressed by leveraging SaaS Management tools, securing leadership buy-in, and implementing a phased rationalization approach.
Cloud migration rationalization involves evaluating which applications should be moved to the cloud, rehosted, or replaced with cloud-native solutions to optimize performance and cost.
Rationalization aligns IT strategy with business goals by eliminating redundant applications, improving system integration, and ensuring technology investments support long-term growth.
Organizations can cut unnecessary software spending, reduce license waste, and streamline IT operations by identifying unused or redundant applications.
Ignoring rationalization can lead to excessive SaaS spending, security vulnerabilities, compliance issues, and inefficiencies that hinder business performance.
Rationalization reduces complexity, which improves efficiency across teams. At the same time, it eliminates unnecessary spend, giving you room to reinvest in other strategic initiatives.
Common hurdles include siloed ownership of applications, cultural resistance to change, and incomplete visibility. Addressing these proactively helps you avoid roadblocks.
Prioritization comes from reviewing usage, cost, security, and alignment with goals. A structured framework helps you distinguish between valuable applications and those that offer minimal value.
The Gartner TIME model (Tolerate, Invest, Migrate, Eliminate) provides a framework to classify applications. It helps you make decisions based on value and risk rather than guesswork.

Table of Contents ToggleWhat Are Longtail SaaS Applications?The Rise of Longtail...

Table of Contents ToggleEpisode SummaryGuest SpotlightEpisode HighlightsSourcing Teams Are Key to...

Table of Contents ToggleWhat Is Technology App Rationalization?Application Rationalization BenefitsWhat Drives...

In the past 4 years, Adobe has rapidly scaled from $9B to $18B. This growth has made an already complex environment even more complex. Learn how they leveraged Zylo to get complete visibility into their SaaS portfolio, unlock millions in cost savings and avoidance and improve the employee experience.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |